Fig. 3.
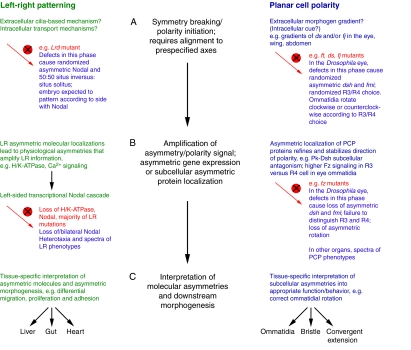
LR patterning and PCP steps share similar logic. Three phases of patterning required for LR asymmetry (left, green) and PCP (right, blue). The mutant vertebrate LR and Drosophila PCP eye phenotypes that result from disruption (red circle with a cross) of each phase are described. For simplicity, we focus on phenotypes that result from mutations in PCP genes in the ommatidia of the Drosophila eye. (The details of analogous phenotypes between the phases of LR and PCP establishment might differ in other planar-polarized epithelia.) (A) In the first phase, symmetry breaking and polarity initiation occur. Defects in this phase abolish the directional cue and lead to random selection of polarity direction, resulting in mutants that retain asymmetric, but randomly oriented, expression of key downstream genes such as Nodal and fz. Mutants develop with randomized asymmetry/polarity that follows from the direction of asymmetric gene expression. For example, 50:50 situs inversus:situs solitus in LR left-right dynein (Lrd) mutant or randomized clockwise/counterclockwise rotation of ommatidia in PCP fat (ft), dachsous (ds) and four-jointed (fj) mutants. (B) In the second phase, the asymmetry/polarity cue is amplified and refined over the cell field. In LR patterning, this might occur via asymmetric ion flux or movement of extracellular morphogens by cilia that are ultimately transduced into the left-sided Nodal transcriptional cascade. In PCP, this occurs via the asymmetric subcellular localization of PCP proteins. Mutations in this phase often cause loss of asymmetric gene expression and a spectrum of LR and PCP phenotypes [loss of, or bilateral, Nodal expression and heterotaxia in LR patterning, or loss of asymmetric Frizzled (Fz) and loss of asymmetric rotation in ommatidia, respectively]. (C) In the final phase, the molecular asymmetries are differentially interpreted in the individual tissues to produce the required morphologies. Mechanisms and phenotypes are reviewed elsewhere (Levin, 2006; Seifert and Mlodzik, 2007; Tree et al., 2002a; Wang and Nathans, 2007; Zallen, 2007). pk, prickled; dsh, dishevelled; fmi, flamingo; R, photoreceptor.