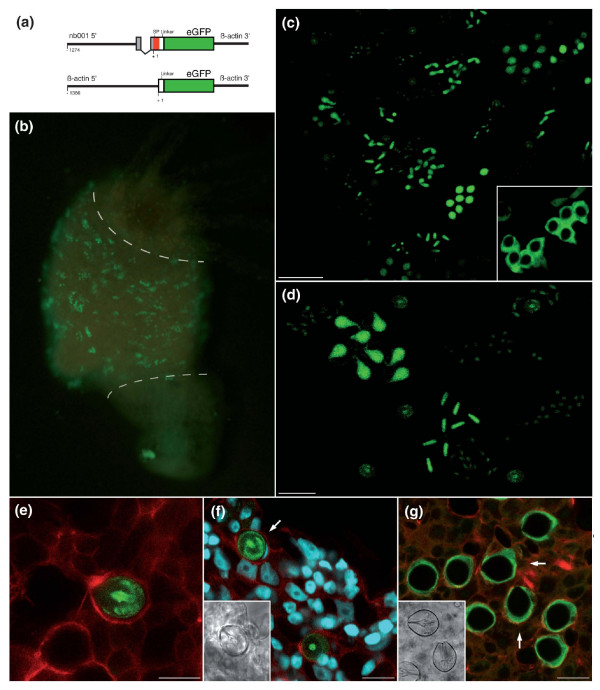
Figure 10.
Functional analysis of the nb001 promoter using transgenic polyps. (a) Expression constructs for generation of transgenic Hydra (SP, signal peptide). (b) Polyp with eGFP-expressing differentiating nematocytes. Note that the nb001 driven eGFP expression recapitulates the nb001 expression shown in Figure 2a. As indicated by the dashed lines, expression is located only in the bodycolumn and not in the head or foot. (c) Confocal analysis of polyp containing eGFP-expressing nematocytes reveals that the promoter drives expression of eGFP in all four types of nematocytes; scale bar, 50 μm. The inset indicates control transgenic nematocytes with eGFP expression under control of actin promoter. (d) Transgenic nematocytes provide in vivo evidence for the view [28] that differentiating nematocytes undergo several rounds of synchronous cell division and remain connected to each other by cytoplasmic bridges to form nests of 4, 8 or more cells; scale bar, 25 μm. (e) Tentacle of transgenic polyp in which many but not all nematocytes are expressing eGFP. Confocal analysis. Green, eGFP protein; red, actin filaments; scale bar, 10 μm. (f) Confocal analysis of transgenic stenotele (arrow) in the gastric region showing eGFP protein localized within the capsule wall and tubule of the nematocyst. Red, actin filaments; scale bar, 15 μm. (g) Control transgenic polyp with eGFP expression under control of actin promoter. Note that eGFP is localized within the cytoplasm and the nematocyst is eGFP negative (arrows). Green, eGFP protein; red, actin filaments; scale bar, 15 μm.