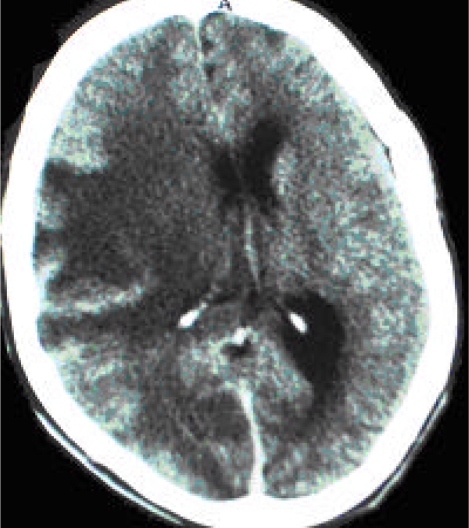
Figure 1.
CT scan (post-contrast) of patient KE showing an extensive ill-defined, non-enhancing hypodense lesion involving most of the right parietal lobe with global sulcial effacement, right lateral ventricle compression with 0.9 cm mid-line shift. Findings are suggestive of an inflammatory cerebral lesion with massive brain edema with imminent danger of infratentorial coning. Possible differential diagnoses include toxoplasmosis, TBM, and cerebral brain abscess.