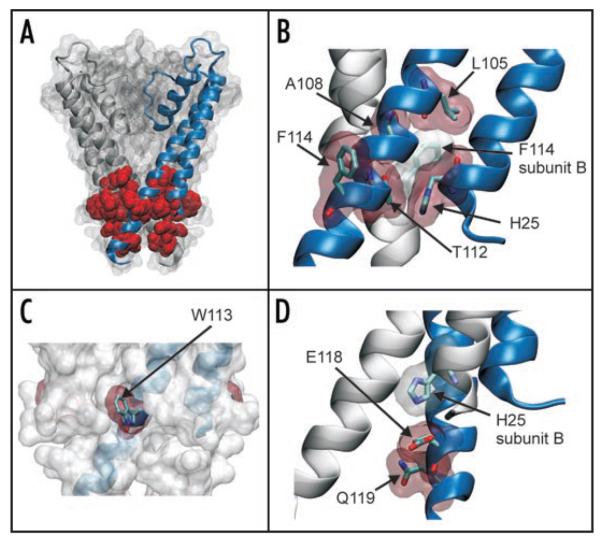
Figure 4.
Location of activatory mutations in the structure of KcsA. (A) The mutations identified in this study are mapped onto the structure of KcsA (PDB: 1K4C). For clarity the structure is shown as a surface map with only two subunits highlighted. The 8 residues (H25, L105, A108, T112, W113, F114, E118 and Q119) on all four subunits are shown in red as vdw spheres. All of these residues are located at the helix-bundle crossing. (B) Expanded view showing that residues H25, L105, A108, T112 and F114 all pack tightly at the helix-bundle crossing. Residues are shown as sticks with a vdw outline. In particular it can be seen how these residues pack tightly with F114 from an adjacent subunit. (C) The helix-bundle crossing is show as a vdw outline with one subunit highlighted. All four W113 residues are shown in red and can be seen to protrude from the surface of the channel. (D) Residues E118 and Q119 are below the helix-bundle-crossing. As shown previously,25 H25 H-bonds with E118 on an adjacent subunit forming part of the pH-gating mechanism. Q119 resides below and the side chain faces into the pore of the channel.