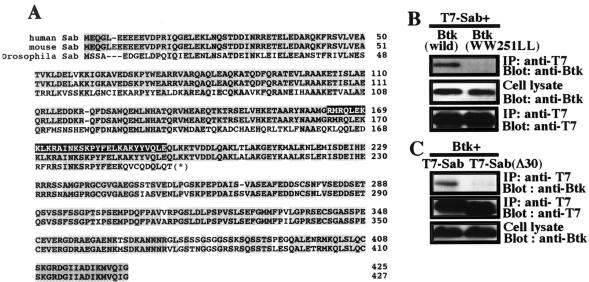
Figure 1.
(A) Amino acid sequences of human, mouse, and Drosophila Sab and the Btk-binding site. The human Sab sequence was reported previously (25). Mouse Sab cDNA was cloned from the C57BL/6 cDNA library, and its sequence has been deposited in the GenBank database (accession no. AB016835). The Drosophila protein sequence was deduced from a 747-bp nucleotide sequence in a Berkeley Drosophila Genome Project/Howard Hughes Medical Institute Drosophila expressed sequence tag (accession no. AA567603) and was hypothesized to be a protein homologous with that of human Sab because of its highly conserved amino acid sequence (48% identity with human Sab in the available sequence). ∗, The C-terminal sequence was not available. The sequences with a gray background indicate identical residues, and those with a black background in the human Sab sequence indicate the minimum region required for the binding to Btk (25). (B and C) Characterization of the in vivo association of Sab and Btk in 293T cells. (B) Wild-type or SH3-mutated Btk (WW251LL) was transiently coexpressed with T7 epitope-tagged Sab. The associations between Sab and Btk were evaluated by immunoprecipitation (IP) with the anti-T7-tag antibody followed by immunoblotting (Blot) with the anti-Btk antibody 43-3B (Top). (Middle and Bottom) Confirmation of the expressions of Btk and T7 epitope-tagged Sab proteins, respectively. (C) T7 epitope-tagged Sab or Sab(Δ30) was coexpressed with wild-type Btk. The associations were evaluated by immunoprecipitation with the anti T7-tag antibody followed by immunoblotting with the anti-Btk antibody 43-3B (Top). (Middle and Bottom) Confirmation of the expressions of T7 epitope-tagged Sab proteins and Btk, respectively.