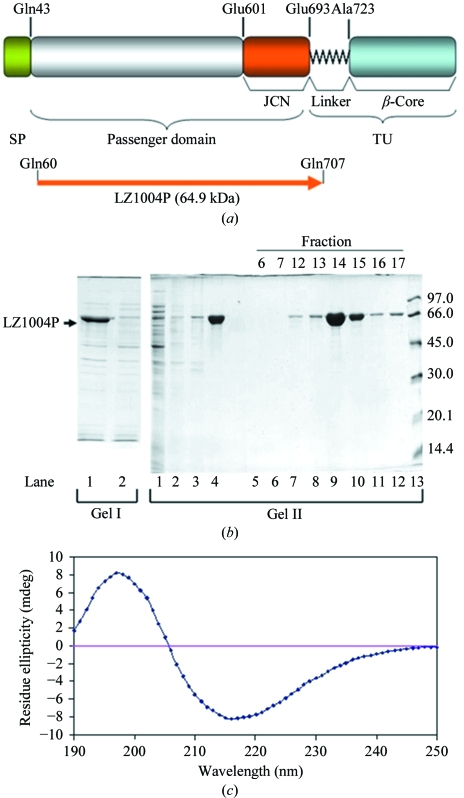
Figure 1.
Expression and purification of the BrkA passenger domain. (a) Domain organization of BrkA (Oliver, Huang & Fernandez, 2003 ▶; Oliver, Huang, Nodel et al., 2003 ▶). SP represents the signal peptide (residues 1–42). The passenger domain contains residues 43–692 and the junction region (JCN) is located at the C-terminus of the passenger domain (residues 601–692). TU represents the translocation unit, which is composed of the linker region (residues 693–731) and the β-core (residues 732–1010). The BrkA passenger domain (LZ1004P) was expressed using a pET expression system. (b) Purification of LZ1004P. Gel I and gel II are from two reproducible purification experiments. Gel I: lane 1, whole cell lysate; lane 2, soluble form of cell lysate. Gel II: lane 1, soluble form of cell lysate. Lanes 2–4 are from the insoluble inclusion bodies after various treatments. Lane 2, supernatant of the inclusion-bodies sample after Triton X-100 wash; lane 3, precipitate removed after dialysis; lane 4, supernatant remaining after dialysis. Lanes 5–12, fractions eluted from Resource Q column. Lane 13, low-molecular-weight markers (labelled in kDa). The majority of the protein was in the supernatant after resolubilization and dialysis and was eluted between NaCl concentrations of 0.21 and 0.25 M. (c) Far-UV circular-dichroism spectrum of 0.15 mg ml−1 LZ1004P in 20 mM phosphate buffer pH 7.5.