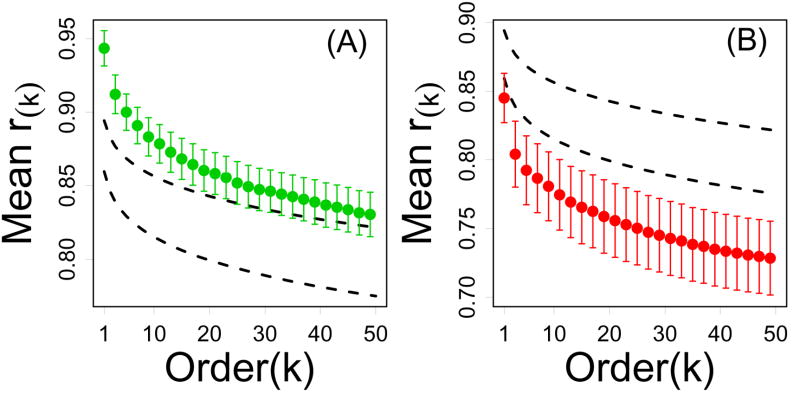
Figure 4.
Local connectivity of CR-regulated genes (Treatment series). In each plot, the vertical axis represents the average kth correlation order statistic (among n genes) and the horizontal axis corresponds to k. For a given gene, the kth correlation order statistic equals the kth largest correlation between that gene and all other transcripts represented on the Affymetrix Mouse Genome 430 2.0 array. Highly connected genes should have larger correlation order statistics for a given value of k, where the decay with increasing k indicates the decline in connection strength to increasingly distant network neighbors. In part (A), green points represent the average kth correlation order statistic among the n = 12 CR-downregulated genes. In part (B), red points represent the average kth correlation order statistic among the n = 16 CR-upregulated genes. In both (A) and (B), dashed black lines outline a 95% confidence region for the average kth correlation order statistic among n genes sampled at random (based upon simulation). In 95% of 10,000 simulation trials, random samples of n genes from the Affymetrix Mouse 430 2.0 array yielded an average kth correlation order statistic within the dashed lines. Results shown were generated from the Treatment series, but similar results were obtained based on the Tissue, Developmental and Mutation series (see Supplemental Data File 5).