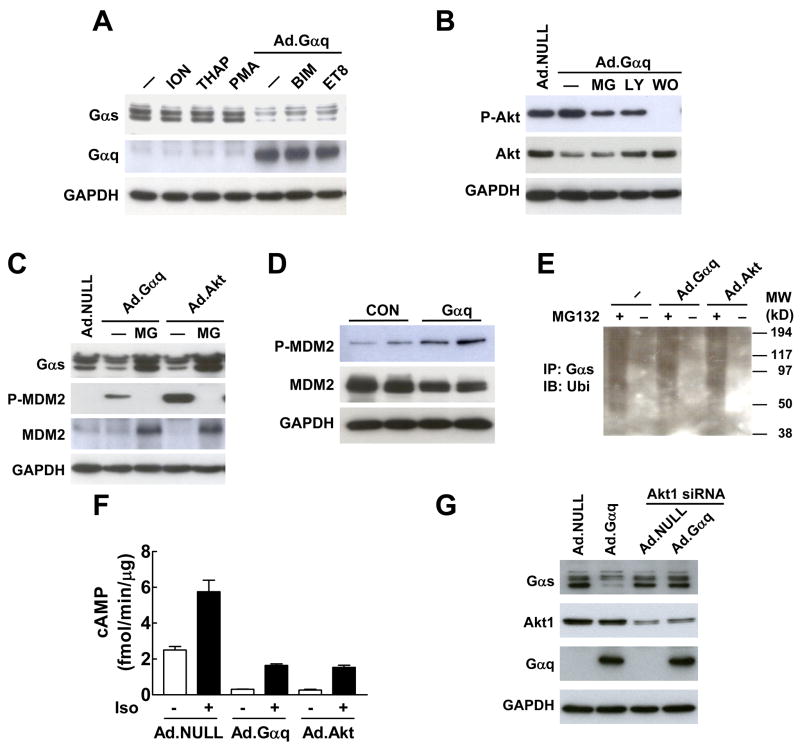
Fig. 3.
Gαq-induced Gαs protein degradation is mediated by Akt. (A) Gαq-induced reduction in Gαs protein was not mediated by Ca2+ activators ionomycin (ION) and thapsigarin (THAP), PKC activator PMA, and PKC inhibitors BMI and Et-8-OCH3 (ET8). (B) PI3K inhibitors LY294002 (LY) and wortmanin (WO) inhibited Gαq-induced Akt activation. MG, MG132. (C) Expression of Gαq and constitutively active Akt in HEK293 cells decreased Gαs protein content and increased MDM2 phosphorylation. Treatment with the proteasomal inhibitor MG132 (MG) blocked the reduction of Gαs protein content. (D) Cardiac-directed Gαq expression increased MDM2 phosphorylation in LV samples. (E) Expression of constitutively active Akt (Ad.Akt) increased Gαs ubiquitination in HEK293 cells. Endogenous Gαs-ubiquitin conjugate was co-immunoprecipitated by Gαs antibody and detected by Western blotting using ubiquitin antibody. (F) Expression of Gαq and constitutively active Akt decreased basal and isoproterenol (Iso)-stimulated cAMP production in isolated neonatal cardiac fibroblasts. Bars represent mean values from six experiments and error bars denote SEM (n=6). (G) Knockdown of Akt1 by siRNA blocked Gαq-induced reduction in Gαs protein.