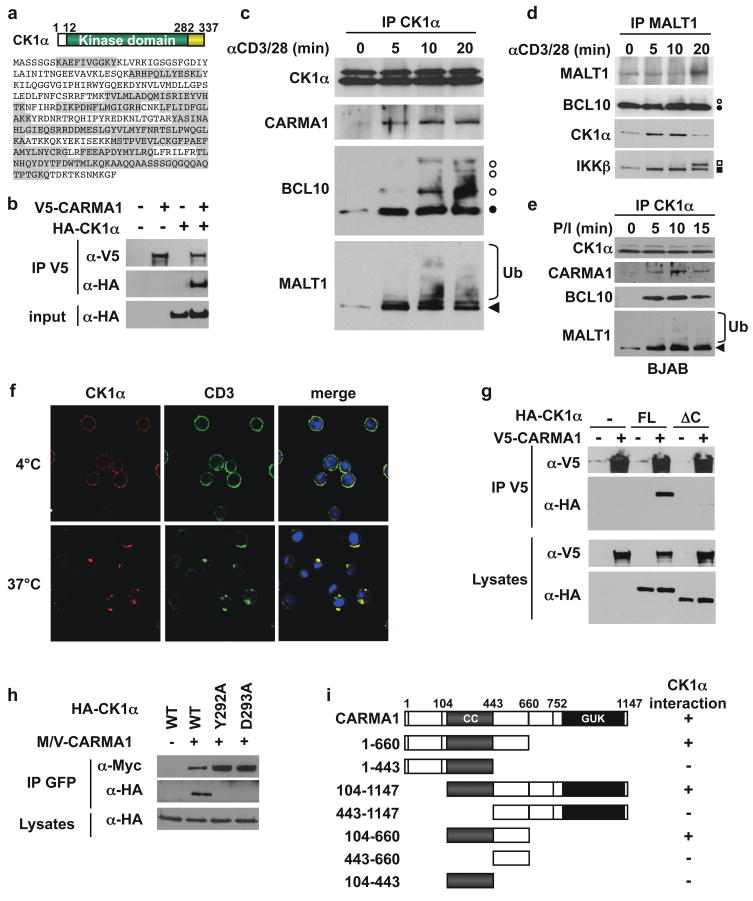
Figure 1. Identification of CK1α as a CARMA1-binding partner.
a, Schematic and sequence of CK1α. Peptides identified by a mass spectrometry analysis of CARMA1-containing complexes are highlighted in grey. b, Interaction between HA-CK1α and V5-CARMA1 in HEK293T cells by immunoprecipitation (IP) and immunoblot (IB). c–e, IP/IB as indicated, in Jurkat T lymphocytes stimulated with 1 μg/ml anti-CD3 and anti-CD28 (c–d), and in BJAB B cells stimulated with 20 ng/ml PMA and 300 ng/ml ionomycin (e). Filled and open symbols, non phosphorylated and phosphorylated forms. Ub, ubiquitin. f, Confocal images of CD3 and CK1α following CD3 crosslinking in Jurkat. Nuclei counterstaining is shown in blue. g, IP/IB of V5- CARMA1 binding to HA-tagged CK1α full-length (FL) or lacking residues 283-337 (ΔC) in HEK293T cells. h, Myc-Venus (M/V)-tagged CARMA1 association with HA-CK1α mutants in HEK293T cells by IP/IB. i, Mapping of the minimal CK1α-binding domain of CARMA1 by IP/IB in HEK293T cells expressing HA-CK1α and M/V-CARMA1 truncation mutants.