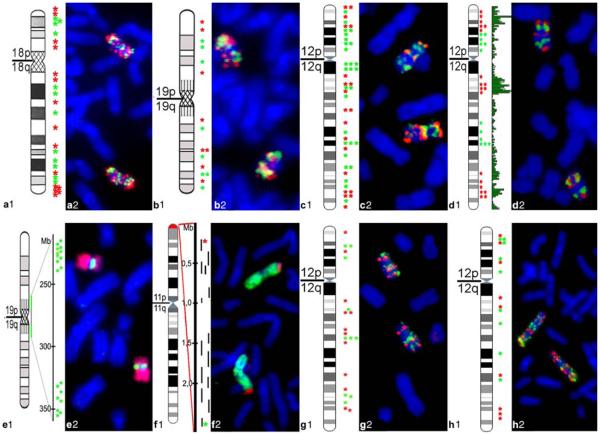
Fig. 1.
Overview of BAC pools. Panels a1–h1 denote the chromosomal position of each BAC (marked by an asterisk) used in this study with the corresponding idiogram at 850-band resolution. Panels a2–h2 show respective FISH control experiments on metaphase chromosomes (blue). a R/G-band-assigned BAC pool of HSA 18 comprising 12 BACs from G-dark (G) bands (green) and 15 BACs from G-light (R) bands (red). b R/G-band-assigned BAC pool of HSA 19 comprising 8 BACs from G-dark (G) bands (green) and 8 BACs from G-light (R) bands (red). c R/G-band-assigned BAC pool of HSA 12 comprising 28 BACs from G-dark (G) bands (green) and 20 BACs from G-light (R) bands (red). d Gene-density-assigned BAC pool of HSA 12 comprising 19 BACs of gene-dense segments (red) and 12 BACs from gene-poor segments (green). The green bars delineate the gene content along the chromosome. e Gene-density-assigned BAC pool of HSA 19 representing segments of the gene-poor region 19p12–19q12 comprising 19 BACs (green). HSA 19 are painted in red in E2. f BAC pool delineating a gene-dense segment of 11p15.5 comprising 14 BACs. The exact position of each BAC is represented by a black bar in f1; the BAC contig is visualized in red and the painted HSA 11 in green in f2. g–h Expression-assigned BAC pools of HSA 12 in Hly (g) and Hfb (h) comprising 10 (Hly) and 9 (Hfb) BACs with weakly expressed genes (green) and 12 (Hly) and 9 (Hfb) BACs with highly expressed genes (red)