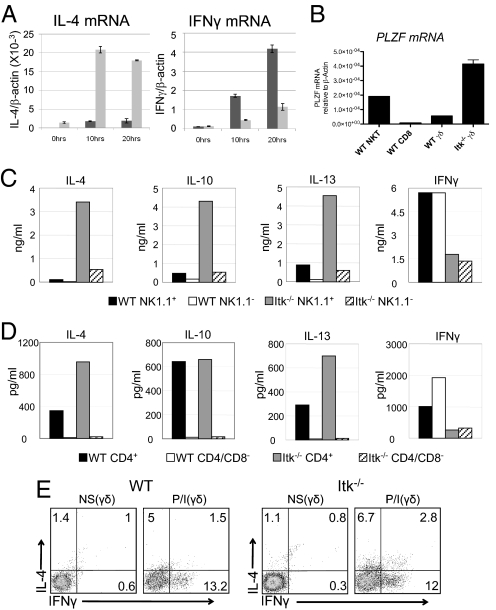
Fig. 4.
Itk−/− γδ T cells produce IL-4 plus IFN-γ and express the transcription factor PLZF. Lymph nodes and spleens from WT and Itk−/− mice were pooled, and total TCRγδ+ cells (A, B) or sorted subpopulations (C, D) were analyzed. (A) 2 × 105 cells were stimulated with 10 μg/ml of anti-TCRδ for 0, 10, and 20 hours. IL-4 (left panel) and IFNγ (right panel) mRNA expression levels normalized to β-actin were determined by real-time quantitative RT-PCR. Data shown are representative of two independent experiments. (B) Levels of PLZF mRNA normalized to β-actin were determined by real-time quantitative RT-PCR. WT peripheral CD8+ αβ T cells and αβ NKT cells were analyzed for comparison. Data are representative of two independent experiments. (C) 5 × 104 cells were stimulated with 10 μg/ml of anti-TCRδ for 72 hours and supernatants were analyzed for the presence of IL-4, IL-10, IL-13, and IFNγ by cytometric bead array (CBA). Data are representative of three independent experiments. (D) 3 × 104 cells were stimulated as in (B). Supernatants were analyzed for the presence of IL-4, IL-10, IL-13, and IFNγ by CBA. Data are representative of two independent experiments. (E) Nonstimulated (NS) and stimulated (P/I) WT (left) and Itk−/− (right) γδ T cells were analyzed for intracellular IL-4 and IFN-γ production. Cells were stimulated with 10 ng/ml PMA and 2 μg/ml Ionomycin (P/I) for 4 hours. Data are representative of four independent experiments.