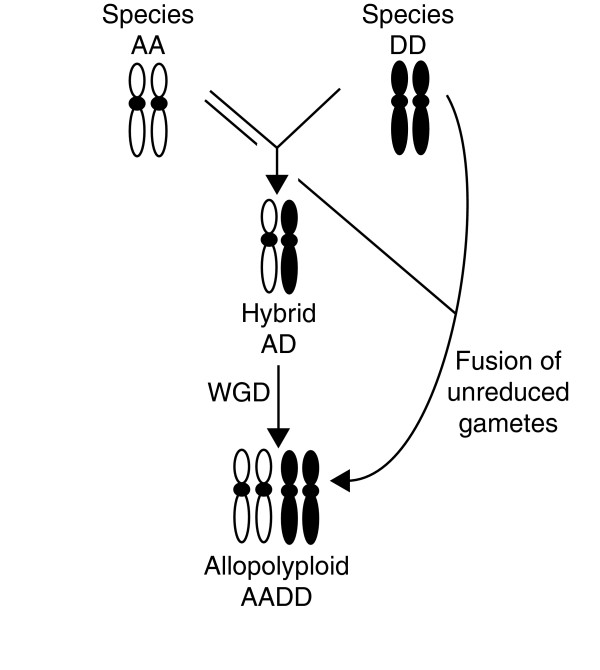
Figure 1.
Mechanisms of polyploid formation. For simplicity, the A and D genomes of the diploid species are represented by only two chromosomes, in white and black, respectively. An allopolyploid (AADD) may form as a result of hybridization of the two species (hybrid AD), followed by whole-genome duplication (WGD). Alternatively, the two diploid species may give rise directly to the allopolyploid by fusion of their unreduced gametes.