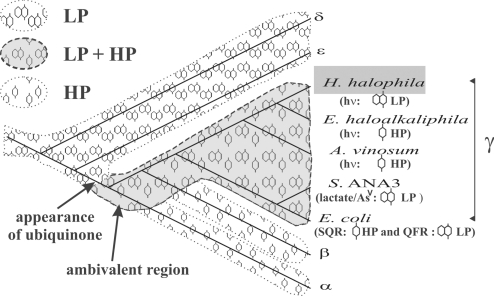
Fig. 4.
Distribution of MK- and UQ-based chains on a proteobacterial phylogenetic tree. This tree (reconstructed by the neighbor-joining method) is based on 16S r-RNA genes. The shaded area indicates extant and extinct lineages where both MK and UQ functioned alternatively. The probable evolutionary appearance of the UQ molecule after the divergence of the δ- and ε-subgroups and before the α/β/γ-radiation is indicated. The α, β, δ, and ε species used for the tree reconstruction are, Rhodobacter sphaeroides, Rubrivivax gelatinosus, EbS7, and Helicobacter pylori, respectively. Identification of HP and/or LP chains are based on our work for H. halophila, on refs. 10, 28, and 29 for E. haloalkaliphila, on refs. 11, 26, and 27 for A. vinosum, on ref. 30 for Shewanella ANA-3, and on ref. 12 for E. coli.