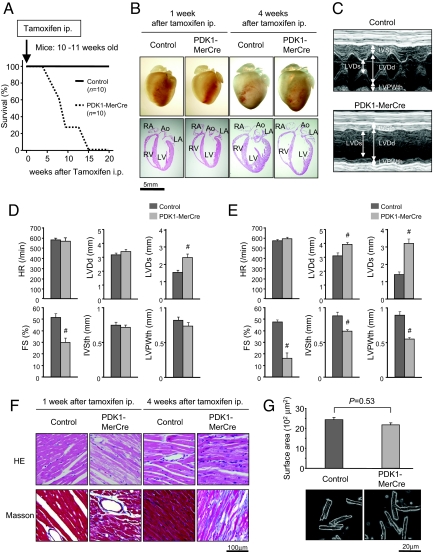
Fig. 1.
Severe heart failure observed in PDK1-MerCre mice. (A) Kaplan-Meier survival curves of PDK1-MerCre mice (n = 10) and control mice (n = 10). Mice were injected with tamoxifen at the age of 10–11 weeks. (B) Macroscopic findings and 4-chamber sections of the hearts from PDK1-MerCre and control mice 1 and 4 weeks after the initiation of tamoxifen treatment. Ao, aorta; LA, left atrium; LV, left ventricule; RA, right atrium; RV, right ventricule. (C) Representative M-mode echocardiograms of mice 1 week after tamoxifen treatment. (D) Echocardiographic measurements of PDK1-MerCre and control mice 1 week after tamoxifen treatment. HR, heart rate; LVDd, LV dimension in diastole; LVDs, LV dimension in systole; FS, fractional shortening; IVSth, interventricular septum thickness; LVPWth, LV posterior wall thickness. Values represent the mean ± SEM of data from 10 mice in each group. #, P < 0.01 versus control group. (E) Echocardiographic measurements of PDK1-MerCre and control mice 4 weeks after tamoxifen treatment. Values represent the mean ± SEM of data from 6 mice in each group. #, P < 0.01 versus control group. (F) Histological sections with hematoxylin and eosin (HE) staining and Masson's trichrome (Masson) staining of PDK1-MerCre and control mice 1 and 4 weeks after tamoxifen treatment. (G) Surface areas of isolated cardiomyocytes (57 individual cardiomyocytes in each group) and sample pictures of isolated cardiomyocytes from PDK1-MerCre and control mice 1 week after tamoxifen treatment. Values represent the mean ± SEM.