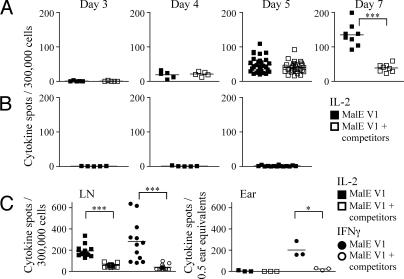
Fig. 5.
Abortive CD4 T cell expansion to low-stability peptide:class II complexes. Mice were immunized in the ear with 10 μL of 25 nmol of MalE V1 in an emulsion containing IFA/PBS and 0.6 μg/mL LPS alone or in a mixture with 5 nmol of the dominant peptides MalE[102-115], OVA V3, and MYO[102-118]. At days 3, 4, 5, 7, and 10, CD4 T cells purified by negative selection from deep cervical LNs (A and C) or unpurified ear pinnae tissue extract (C) were restimulated with 20 μM of the test peptide in the presence of T cell depleted splenocytes in IL-2 (A–C, □) and IFNγ (C, ○) ELISpot assays. There was no antigen-specific T cell response detected at the peripheral site of immunization before day 7. (B) Response of CD4 T cells purified from LN of mice immunized with IFA/LPS at the early time points for production of IL-2 when restimulated with 20 μM of the test peptide. CD4 T cells enriched from the LN were plated at 300,000 cells/well, and unpurified cell suspensions from the ear were plated at 0.5 ear equivalents/well. Draining LNs from individual mice were pooled and there were 5 mice per group. The results are presented as the number of cytokine spots/300,000 T cells per pooled LN of individual mice from triplicate wells or as the number of cytokine spots/0.5 ear equivalents from triplicate wells at each time point, with the mean number of spots indicated. Results were analyzed with the 1-way Student's t test; *, P < 0.05; ***, P < 0.0005.