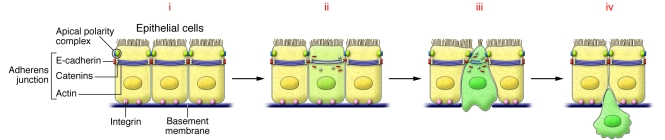
Figure 1. Cellular aspects of EMT.
(i) Normal epithelial cells contain adherens junctions composed of E-cadherin together with catenins and actin rings. Tight junctions are associated with apical polarity complexes, while integrins interact with components of the basal membrane. (ii) Loss of cell-cell adhesion. EMT inducers repress the transcription of the genes encoding the components of both adherens and tight junctions, inducing the loss of cell polarity. E-cadherin is internalized and targeted for degradation. (iii) Breakdown of the basal membrane and apical constriction. Profound cytoskeletal remodeling will favor cell delamination by inducing apical constriction and disorganization of the basal membrane. (iv) Cell delamination and invasion. Expression of integrin receptors and continued activation of metalloproteases favors migration through the extracellular matrix and invasion of adjacent tissues.