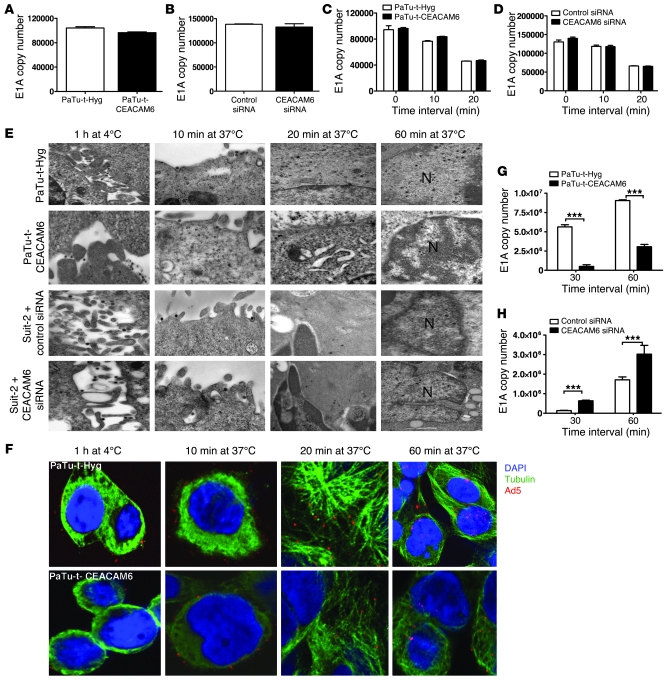
Figure 4. Effect of CEACAM6 on the life cycle of adenovirus.
(A) Quantitation of E1A copy number after Ad5 binding in PaTu8988t-Hyg and PaTu8988t-CEACAM6 cells at 4°C for 1 hour (P = 0.5679) by qPCR. (B) qPCR quantitation of E1A copy number after Ad5 binding in control and CEACAM6-specific SMARTpool siRNA–pretreated Suit-2 cells at 4°C for 1 hour (P = 0.3619). (C) qPCR quantitation of E1A copy number of uninternalized adenovirus in PaTu8988t-Hyg and PaTu8988t-CEACAM6 cells (P > 0.05) at different time points. (D) qPCR quantitation of E1A copy number of uninternalized adenovirus in control and CEACAM6-specific SMARTpool siRNA–treated Suit-2 cells (P > 0.05) at different time points. (E) Adenovirus attachment and trafficking observed by TEM in CEACAM6-modulated cells and their counterparts after Ad5 was allowed to bind at 4°C for 1 hour and allowed to internalize and traffic to the nuclei at 37°C for various time points. N, nucleus. Original magnification, ×60,000. (F) Confocal images of stable cells with labeled Ad5 particle (red) and α-tubulin (green) after Ad5 was bound at 4°C for 1 hour and allowed to internalize and traffic to nuclei at 37°C for various times; original magnification, ×600. (G) Quantitation of E1A copy number in the nucleus after Ad5 was bound at 4°C for 1 hour and allowed to traffic at 37°C for 30 and 60 minutes in PaTu8988t-Hyg and PaTu8988t-CEACAM6 cells by qPCR. (H) qPCR quantitation of E1A copy number in the nuclei after Ad5 was allowed to bind at 4°C for 1 hour and allowed to traffic at 37°C for 30 and 60 minutes in control and CEACAM6-specific siRNA–treated Suit-2 cells by qPCR. ***P < 0.001.