Figure 9.
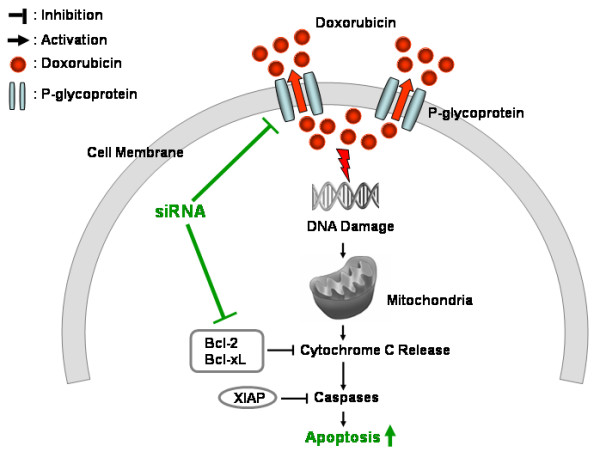
Doxorubicin resistance mechanisms in chondrosarcoma cells. A schematic diagram demonstrates a molecular pathway of apoptosis that is triggered by doxorubicin. Doxorubicin damages DNA. This DNA damage induces cytochorome C release in mitochondria which activates caspases, the effectors of apoptosis. P-glycoprotein inhibits doxorubicin effect by drug efflux. Bcl-2 and Bcl-xL block cytochrome c release. XIAP inhibits caspase activation.
