Abstract
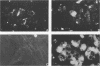
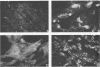
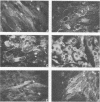
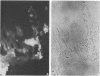
This paper describes an improved method for the in vitro detection of antibodies specifically directed against human cytomegalovirus (CMV)-induced membrane antigens present on the surface of CMV-infected fibroblasts (CMV-MA). Viable cells were found to be essential for specific visualization of CMV-MA staining. The addition of divalent cations (2.6 mM Ca2+ and 2.2 mM Mg2+) and glucose (180 mM) to the incubation and washing buffers improved the viability and morphology of the cells and increased the cell yield at the end of the assay. Clustering of antigen-antibody complexes on the surface of viable CMV-infected cells was prevented by low-temperature incubation (0 to 4 degrees C) rather than by the addition of agents which act on the metabolism of the cell. No interaction with the CMV-induced Fc receptor was observed at 0 degrees C with either human sera or murine monoclonal antibodies. The specificity of the CMV-MA reaction was confirmed by using monoclonal antibodies to CMV nuclear, cytoplasmic, and membrane-associated antigens. Furthermore, a microplate modification of the membrane fluorescence test is described which is suitable for multisample screening purposes. This method can be applied to the determination of anti-CMV-MA antibody titers in human sera and to the screening of hybridoma supernatants for the presence of antibodies with specificity for CMV-MA.
Full text
PDF








Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Betts R. F., Schmidt S. G. Cytolytic IgM antibody to cytomegalovirus in primary cytomegalovirus infection in humans. J Infect Dis. 1981 Jun;143(6):821–826. doi: 10.1093/infdis/143.6.821. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boldogh I., Gönczöl E., Váczi L. Cytomegalovirus-induced membrane antigens in productively infected cells. Acta Microbiol Acad Sci Hung. 1977;24(1):21–28. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boom R., Geelen J. L., Sol C. J., Raap A. K., Minnaar R. P., Klaver B. P., van der Noordaa J. Establishment of a rat cell line inducible for the expression of human cytomegalovirus immediate-early gene products by protein synthesis inhibition. J Virol. 1986 Jun;58(3):851–859. doi: 10.1128/jvi.58.3.851-859.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chiba S., Motokawa T., Tamura T., Hanazono H., Kamada M., Chiba Y., Nakao T. Seroconversion to virus-specific pre-early nuclear antigens in infants with primary cytomegalovirus infection. Infect Immun. 1980 Oct;30(1):135–139. doi: 10.1128/iai.30.1.135-139.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clark B. R., Zaia J. A., Balce-Directo L., Ting Y. P. Isolation and partial chemical characterization of a 64,000-dalton glycoprotein of human cytomegalovirus. J Virol. 1984 Jan;49(1):279–282. doi: 10.1128/jvi.49.1.279-282.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- De Leij L., Poppema S., The T. H. Cryopreservation of newly formed hybridomas. J Immunol Methods. 1983 Aug 12;62(1):69–72. doi: 10.1016/0022-1759(83)90111-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frey J., Einsfelder B. Induction of surface IgG receptors in cytomegalovirus-infected human fibroblasts. Eur J Biochem. 1984 Jan 2;138(1):213–216. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1984.tb07903.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haikin H., Sarov I. Immunoperoxidase antibody to human cytomegalovirus-induced membrane antigen assay in the absence of interfering immunoglobulin G receptors. Intervirology. 1980;14(3-4):155–159. doi: 10.1159/000149177. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huet C., Ash J. F., Singer S. J. The antibody-induced clustering and endocytosis of HLA antigens on cultured human fibroblasts. Cell. 1980 Sep;21(2):429–438. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(80)90479-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lamy M. E., Favart A. M., Leclercq M. F., Segas M., Mendez M., Lhoir C., Cornu C., Burtonboy G. Epstein-barr virus VCA IgM and EBNA IgG antibodies titered by immunofluorescence in microplates. A semi-automated method based on microtiter system. Med Microbiol Immunol. 1982;170(4):247–253. doi: 10.1007/BF02123315. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Middeldorp J. M., Jongsma J., The T. H. Cytomegalovirus early and late membrane antigens detected by antibodies in human convalescent sera. J Virol. 1985 Apr;54(1):240–244. doi: 10.1128/jvi.54.1.240-244.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Middeldorp J. M., Jongsma J., The T. H. Killing of human cytomegalovirus-infected fibroblasts by antiviral antibody and complement. J Infect Dis. 1986 Jan;153(1):48–55. doi: 10.1093/infdis/153.1.48. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Middeldorp J. M., Jongsma J., ter Haar A., Schirm J., The T. H. Detection of immunoglobulin M and G antibodies against cytomegalovirus early and late antigens by enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay. J Clin Microbiol. 1984 Oct;20(4):763–771. doi: 10.1128/jcm.20.4.763-771.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Numazaki Y., Oshima T., Tanaka A., Konno T., Tazawa Y., Karita M., Ishii A., Hirota K., Watabe N., Ishida N. Demonstration of IgG EA (early antigen) and IgM MA (membrane antigen) antibodies in CMV infection of healthy infants and in those with liver disease. J Pediatr. 1980 Oct;97(4):545–549. doi: 10.1016/s0022-3476(80)80006-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pereira L., Hoffman M., Gallo D., Cremer N. Monoclonal antibodies to human cytomegalovirus: three surface membrane proteins with unique immunological and electrophoretic properties specify cross-reactive determinants. Infect Immun. 1982 Jun;36(3):924–932. doi: 10.1128/iai.36.3.924-932.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pereira L., Hoffman M., Tatsuno M., Dondero D. Polymorphism of human cytomegalovirus glycoproteins characterized by monoclonal antibodies. Virology. 1984 Nov;139(1):73–86. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(84)90331-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Quinnan G. V., Jr, Kirmani N., Rook A. H., Manischewitz J. F., Jackson L., Moreschi G., Santos G. W., Saral R., Burns W. H. Cytotoxic t cells in cytomegalovirus infection: HLA-restricted T-lymphocyte and non-T-lymphocyte cytotoxic responses correlate with recovery from cytomegalovirus infection in bone-marrow-transplant recipients. N Engl J Med. 1982 Jul 1;307(1):7–13. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198207013070102. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rabinovitch M., DeStefano M. J. Use of the local anesthetic lidocaine for cell harvesting and subcultivation. In Vitro. 1975 Nov-Dec;11(6):379–381. doi: 10.1007/BF02616374. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rahman A. A., Teschner M., Sethi K. K., Brandis H. Appearance of IgG (Fc) receptor(s) on cultured human fibroblasts infected with human cytomegalovirus. J Immunol. 1976 Jul;117(1):253–258. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stinski M. F., Mocarski E. S., Thomsen D. R., Urbanowski M. L. Membrane glycoproteins and antigens induced by human cytomegalovirus. J Gen Virol. 1979 Apr;43(1):119–129. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-43-1-119. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tanaka J., Yabuki Y., Hatano M. Evidence for early membrane antigens in cytomegalovirus-infected cells. J Gen Virol. 1981 Mar;53(Pt 1):157–161. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-53-1-157. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- The T. H., Feltkamp T. E. Conjugation of fluorescein isothiocyanate to antibodies. II. A reproducible method. Immunology. 1970 Jun;18(6):875–881. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- The T. H., Klein G., Langenhuysen M. M. Antibody reactions to virus-specific early antigens (EA) in patients with cytomegalovirus (CMV) infection. Clin Exp Immunol. 1974 Jan;16(1):1-7,9-12. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- The T. H., Langenhuysen M. M. Antibodies against membrane antigens of cytomegalovirus infected cells in sera of patients with a cytomegalovirus infection. Clin Exp Immunol. 1972 Aug;11(4):475–482. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Williams V., Gershon A., Brunell P. A. Serologic response to varicella-zoster membrane antigens measured by direct immunofluorescence. J Infect Dis. 1974 Dec;130(6):669–672. doi: 10.1093/infdis/130.6.669. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zaia J. A., Oxman M. N. Antibody to varicella-zoster virus-induced membrane antigen: immunofluorescence assay using monodisperse glutaraldehyde-fixed target cells. J Infect Dis. 1977 Oct;136(4):519–530. doi: 10.1093/infdis/136.4.519. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]