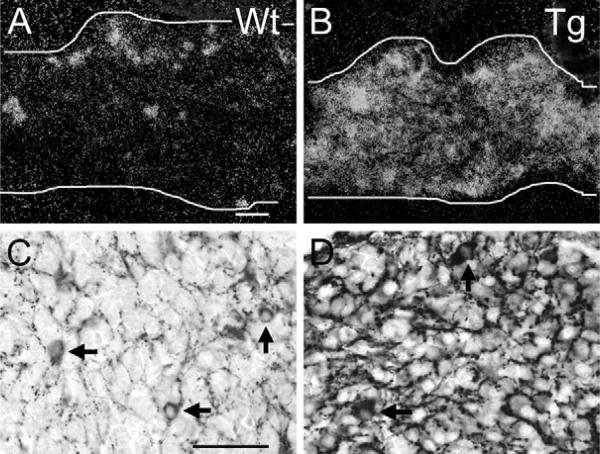
Fig. 4.
VAChT over-expression in SG post-ganglionic neurons and pre-ganglionic input in ChAT-EGFP transgenic mice at P1 as compared with wild type. (A) P1 SG (demarcated by white lines in A, also in B) from a WT mouse. Clusters and single neurons are strongly VAChT ISH-positive. Many additional neurons have weak VAChT mRNA levels. Scale bar=50 μm (A), (also applying to B). (B) P1 SG from ChAT-EGFP transgenic mouse. Many neurons are VAChT ISH-positive. (C) P1 SG from a WT mouse. In addition to the pre-ganglionic input, a few randomly distributed neurons show VAChT immunoreactivity. Scale bar=50 μm (C) (also applying to D). (D) P1 SG from a ChAT-EGFP transgenic mouse. Note stronger immunoreactions in pre-ganglionic fiber input and in a few neuronal cell bodies (arrows) as compared with WT, and weak to intermediate immunoreactions in many other post-ganglionic neurons.