Figure 5.
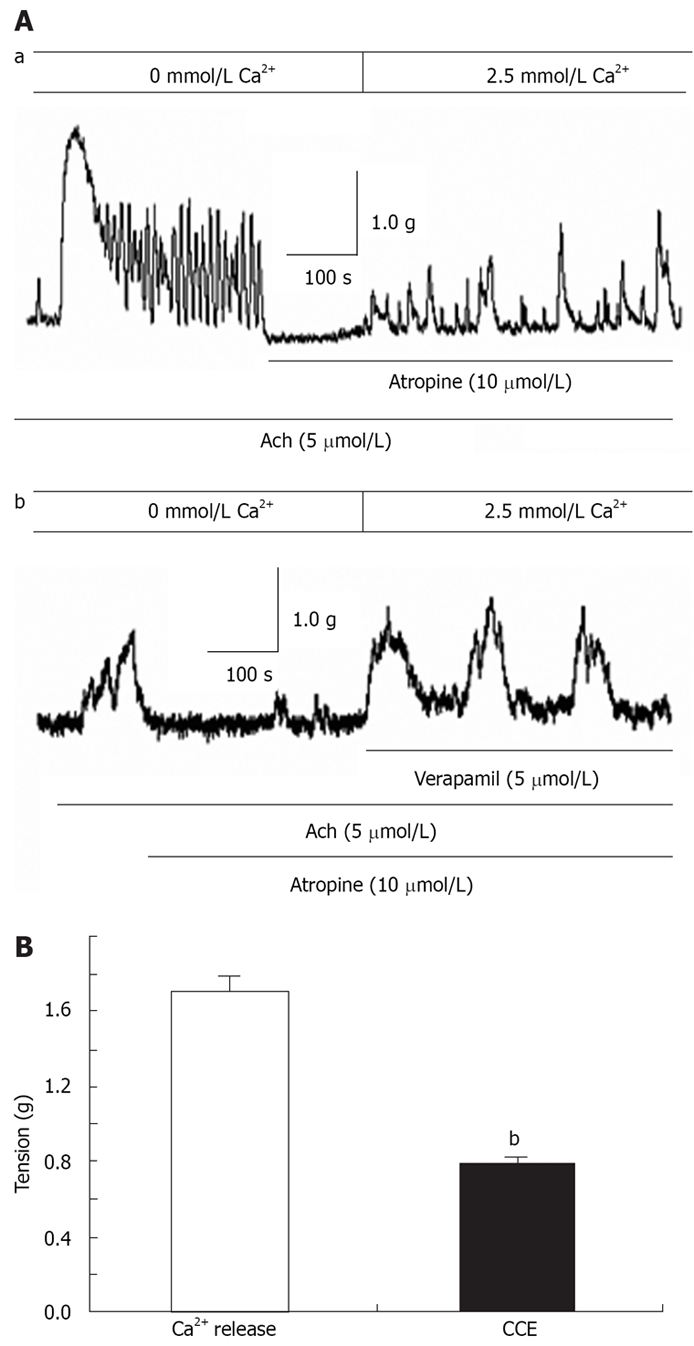
Contribution of Ca2+ release from SR stores and Ca2+ influx via CCE in ACh-induced distal colon contraction. Aa: In the presence of atropine, restoration of extracellular Ca2+ induced contraction, most likely due to Ca2+ influx via CCE; Ab: VOCC blocker verapamil (5 μmol/L) negligibly affected CCE-mediated contraction in the presence of atropine; B: Summarized data showing that CCE-mediated contraction is about 0.46-fold greater than the contraction induced by SR Ca2+ release in ACh-induced rat distal colon contraction. bP < 0.001 vs Ca2+ release.
