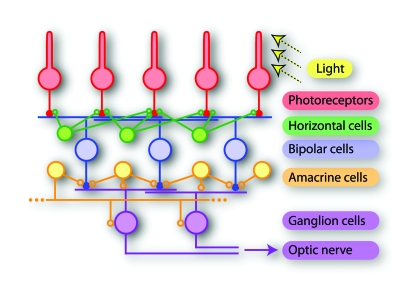
Figure 3. Schematic drawing of the retina network.
Photoreceptors take up light stimuli and transduce them into electrical signals. Bipolar cells constitute a feedforward pathway from the photoreceptors to ganglion cells, which form the output layer of the retina. Horizontal and amacrine cells provide a wealth of additional processing capacities, including lateral inhibition, feedback, and long-range connections. Finally, the visual information is encoded into spike patterns of ganglion cells and transmitted along their axons, which form the optic nerve, to different regions of the brain. Note that the drawing simplifies the actual circuitry, which includes various subtypes of each of the depicted neuron types with specific connection patterns (Masland, 2001; Wässle, 2004). Also, the numerous electrical couplings within the network are left out for clarity.