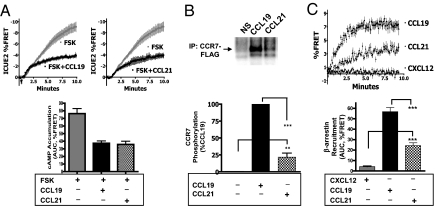
Fig. 1.
CCL19 and CCL21 lead to equivalent G protein responses but differential CCR7 phosphorylation and ß-arrestin2 recruitment. (A) HEK-293 cells stably expressing CCR7 and the cAMP biosensor ICUE2 were stimulated with 50 μM forskolin in the presence or absence of saturating concentrations of CCL19 (100 nM) or CCL21 (100 nM). cAMP accumulation was measured as the change in ICUE2 FRET ratio. (Upper) Change in FRET (mean ± SE, n = 4). (Lower) Integrated response after 10 min. (B) HEK-293 cells stably expressing CCR7-FLAG were labeled with 32Pi and stimulated at 37 °C for 10 min with or without 100 nM CCL19 or 100 nM CCL21 as indicated. (Upper) Representative image showing 32Pi incorporation. (Lower) Bar graph that represents the mean ± SE from six independent experiments. (C) Live HEK-293 cells stably expressing CCR7-CFP and ß-arrestin2-YFP were stimulated with 100 nM CXCL12, 100 nM CCL21, or 100 nM CCL19, and the recruitment of ß-arrestin2 was measured by FRET. Data represent the mean ± SE from six experiments. Statistical significance was determined by paired two-tailed t tests. **, P < 0.01; ***, P < 0.001.