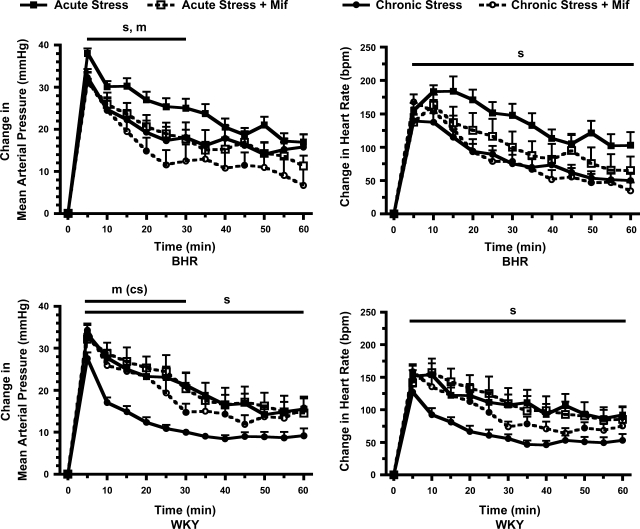
Fig. 2.
Changes in mean arterial pressure (left) and heart rate (right) in response to 60 min of restraint stress in borderline hypertensive rats (BHR) (top) and Wistar-Kyoto (WKY) rats (bottom). Control rats, treated with either a DHB sham pellet or subcutaneous Mif pellet, are shown in solid lines and symbols. DHB Mif-treated rats are shown in dashed lines and open symbols. Chronically stressed rats (circles) were exposed to repeated restraint, while acutely stressed rats (squares) were restrained only on the final day of the experiment. Restraint stress produced a rapid, significant increase in mean arterial pressure and heart rate in all groups of rats (for clarity this statistical significance is not noted in the figure). sP ≤ 0.05 for main effect of chronic compared with acute stress; mP ≤ 0.05 for main effect for control compared with DHB Mif treatment; m(cs)P ≤ 0.05 for significant effect of DHB Mif only in the chronically stressed rats. Baseline values and number of rats per group are in Table 1.