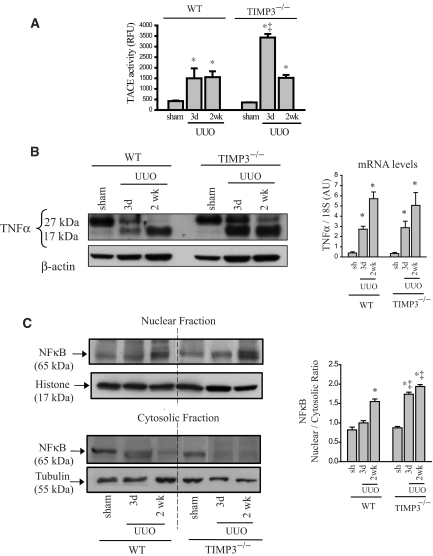
Figure 6.
TNF-α is a key molecule mediating the severe renal injury in tissue inhibitor of matrix metalloproteinases 3 (TIMP3)−/− mice in response to unilateral ureteral obstruction (UUO). (A) Activity of TNFα-converting enzyme (TACE) is significantly increased in (TIMP3)−/− kidneys at 3 d post-UUO but comparable to WT-UUO at 2 wk post-UUO (n = 5). (B) Western blot for TNFα shows the membrane-bound (27 kD) and soluble TNFα (17 kD). Strikingly higher levels of soluble TNFα are detected in TIMP3−/− kidneys at 3 d post-UUO, suggesting enhanced processing of TNFα protein by TACE early after disease in these mice compared with WT (n = 5). TNFα mRNA production is increased similarly in TIMP3−/− and WT kidneys (n = 10 per group). (C) Western blots for NFκB (nuclear factor Kappa-β) on the nuclear and cytosolic fractions show greater nuclear translocation of NFκB in TIMP3−/−-UUO kidneys, as indicated by a higher nuclear-to-cytosolic ratio shown on the right (n = 5). Histone was used as a loading control for the nuclear fraction and tubulin for the cytosolic fraction. Averaged nuclear-to-cytosolic ratio from four blots is shown on the right. *P < 0.05 compared with corresponding sham group. RFU, relative fluorescence units.