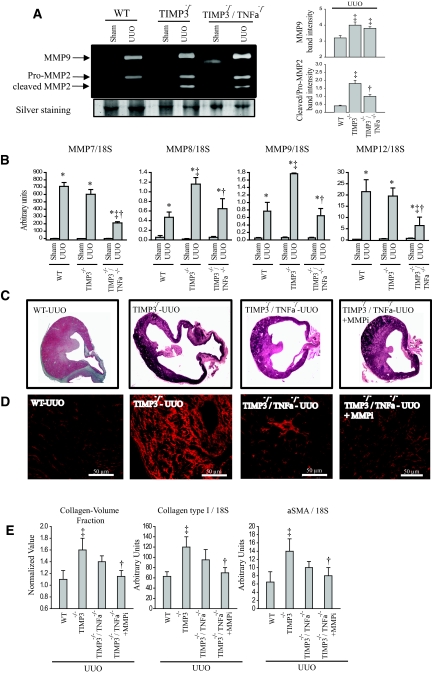
Figure 8.
Inhibition of residual matrix metalloproteinases (MMP) activities in tissue inhibitor of MMP 3 (TIMP3)−/−/TNFα−/− mice further improves after unilateral ureteral obstruction (UUO) injury and fibrosis. (A) Gelatin zymography shows comparable levels of MMP9 and pro-MMP2, but reduced cleaved MMP2 in TIMP3−/−/TNFα−/−-UUO kidneys compared with TIMP3−/−-UUO kidneys, although still higher than WT-UUO group. Averaged band densities for five zymograms are shown on the right. (B) TaqMan real-time PCR analysis of candidate MMPs shows significant reductions in expression of MMP7, MMP8, MMP9, and MMP12 in the TIMP3−/−/TNFα−/− compared with TIMP3−/−-UUO. (C) Representative cross-sectional images of wild-type (WT), TIMP3−/−, TIMP3−/−/TNFα−/−, and TIMP3−/−/TNFα−/− + MMPi (PD166793, a broad-spectrum MMP inhibitor) show a clear improvement in the medullary thickness in the last group. (D) Picrosirius red (PSR) staining and confocal imaging show that tubulointerstitial fibrosis is significantly improved in the double-knock out kidneys and completely blocked with additional MMP inhibition. Collagen-volume fraction (calculated on the basis of the PSR-stained section), production of collagen type I and α-SMA, and markers of fibrosis at 2wk post-UUO are significantly reduced in TIMP3−/−/TNFα−/− + MMPi compared with TIMP3−/− kidneys. *P < 0.05 compared with sham-operated group; ‡P < 0.05 compared with corresponding WT group. †P < 0.05 compared with TIMP3−/− group.