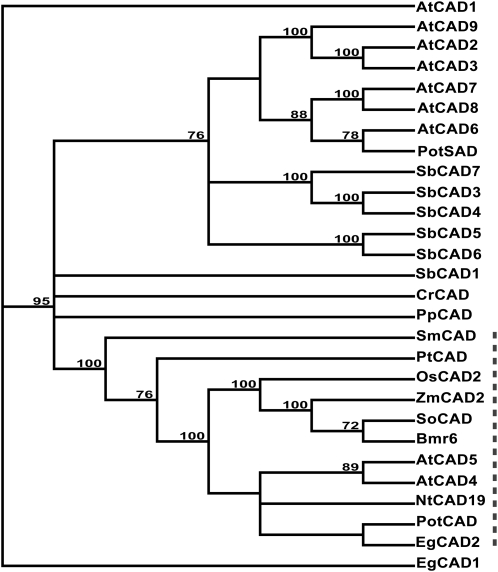
Figure 4.
Phylogenetic analysis of CAD sequences. A phylogenetic tree was created based on predicted amino acids for putative and experimentally demonstrated CADs. The tree was constructed using the Neighbor-Joining method, and the Bootstrap method (1,000 repetitions) was used to estimate the certainty of the branch topography (values given). The GenBank accession number for each amino acid sequence is provided following the name, except for Arabidopsis, Chlamydomonas, Physcomitrella, Selaginella, and Sorghum sequences, whose sequence designation is from their respective genome project. Arabidopsis AtCAD1 (At1g72680), AtCAD2 (At2g21730), AtCAD3 (At2g21890), AtCAD4 (At3g19450), AtCAD5 (At4g34230), AtCAD6 (At4g37970), AtCAD7 (At4g37980), AtCAD8 (At4g37990), and AtCAD9 (At4g39330); aspen PotCAD (AAF43140) and PotSAD (AAK58693); C. reinhardtii CrCAD (CHLREDRAFT_190510); eucalyptus EgCAD1 (CAA61275) and EgCAD2 (CAA46585); loblolly pine PtCAD (CAA86073); maize ZmCAD2 (BM1 locus; NM_001112184); P. patens PpCAD (87951 scaffold_163:497997..49922); rice OsCAD2 (Os02g0187800); S. moellendorffii SmCAD (estExt_fgenesh2_pg.C_390191); sorghum SbCAD1 (Sb06g001430.1), SbCAD3 (Sb02g024210.1), SbCAD4 (Sb02g024190.1), SbCAD5 (Sb07g006090.1), SbCAD6 (Sb06g028240.1), and SbCAD7 (Sb02g024220.1); sugarcane SoCAD (CAA13177); and tobacco NtCAD19 (CAA44217). The dashed line indicates branches of tree containing CAD sequences whose function in monolignol biosynthesis has been genetically and\or biochemically demonstrated.