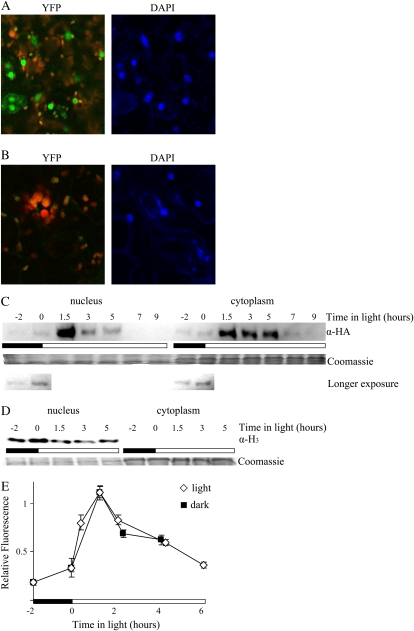
Figure 2.
CCA1-HA-YFP protein can move into the nucleus almost immediately after translation. A and B, Two-week-old CCA1pro∷CCA1-HA-YFP cca1-1#1 (A) and wild-type (B) plants were examined for yellow fluorescence by confocal microscopy 3 h after lights-on. Right panels, DAPI staining (blue) of nuclei; left panels, YFP (green) and chloroplast autofluorescence (red). C and D, Two-week-old CCA1pro∷CCA1-HA-YFP cca1-1#1 plants were grown in LD. Tissue was harvested at intervals starting 2 h before lights-on and the nuclear and cytoplasmic fractions of the cells separated as described in “Materials and Methods.” The levels of CCA1-HA-YFP protein were determined by western analysis with anti-HA antibodies. The Coomassie-stained loading control and a longer exposure of the first two time points (showing that CCA1-HA-YFP is in both the nucleus and cytoplasm 2 h before lights-on) are shown below (C). The levels of histone 3 protein were determined by western analysis with antihistone 3 antibodies (D). E, Two-week-old CCA1pro∷CCA1-HA-YFP cca1-1#1 plants transferred to light or kept in dark were examined at intervals for yellow fluorescence by confocal microscopy. The white and black bars represent light and dark periods, respectively.