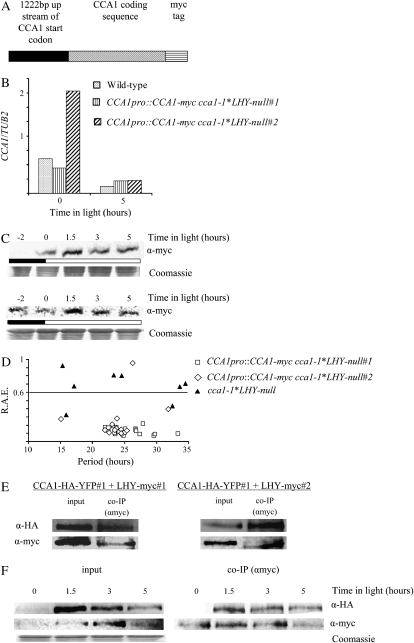
Figure 6.
CCA1 forms homodimers in vivo. A, The CCA1-myc construct used to transform cca1-1*LHY-null plants. B, CCA1pro∷CCA1-myc cca1-1*LHY-null#1, CCA1pro∷CCA1-myc cca1-1*LHY-null#2, and wild-type plants were grown in LD for 2 weeks before being harvested, and the levels of CCA1-myc mRNA and CCA1 mRNA were determined by quantitative PCR and plotted on a graph relative to TUB2 mRNA levels. C, Two-week-old CCA1pro∷CCA1-myc cca1-1*LHY-null#1 and CCA1pro∷CCA1-myc cca1-1*LHY-null#2 plants were grown in LD. The levels of CCA1-myc protein were determined by western analysis. The Coomassie-stained loading control is shown below. The white and black bars represent light and dark periods, respectively. D, One-week-old CCA1pro∷CCA1-myc cca1-1*LHY-null#1, CCA1pro∷CCA1-myc cca1-1*LHY-null#2, and cca1-1*LHY-null plants were transferred to LL after grown in LD. Leaf movements were recorded every 20 min over 7 d and analyzed by FFT-NLLS. The RAE was plotted against the period. E, Four-week-old CCA1pro∷CCA1-myc cca1-1*LHY-null#1;CCA1pro∷CCA1-HA-YFP cca1-1#1 and CCA1pro∷CCA1-myc cca1-1*LHY null#2;CCA1pro∷CCA1-HA-YFP cca1-1#1 plants were grown in LD. Tissue was harvested and used for co-IPs carried out with anti-myc. Proteins were analyzed by western blots with anti-HA (top row) or anti-myc (bottom row). F, CCA1pro∷CCA1-myc cca1-1*LHY null#1;CCA1pro∷CCA1-HA-YFP cca1-1#1 plants were grown in LD for 2 weeks. Tissue was harvested at intervals and used in a co-IP experiment with anti-myc. The proteins were analyzed by western blots with anti-HA (top row) or anti-myc (bottom row). Input, Levels of CCA1-HA-YFP and CCA1-myc in extracts. Co-IP (αmyc), CCA1-HA-YFP and CCA1-myc pulled down by anti-myc antibodies. The Coomassie-stained loading control is shown below.