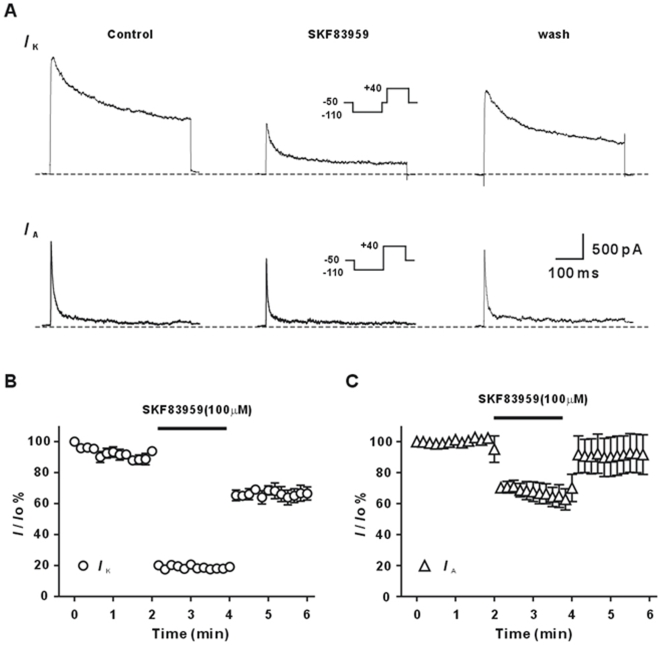
Figure 2. Inhibition of voltage-activated K+ currents by (±) SKF83959 in rat hippocampal neurons.
(A) Upper and lower are the respective representative traces of the delayed rectifier K+ current (I K) and fast transient K+ current (I A) recorded prior to and during superfusion with (±) SKF83959 (100 µM) and after 10 s of washout. The neuron was held at −50 mV. Upper inset shows the pulse protocol to elicit I K, whereas lower inset shows the protocol to elicit the total K+ current. I A is the subtraction of I K from the total K+ current. (B) and (C) Time courses of the inhibition of I K and I A by (±) SKF83959 (100 µM, n = 5 for each). The bar denotes the surpufusion with SKF83959. A number of symbols in (B) and (C) have error bars smaller than their size.