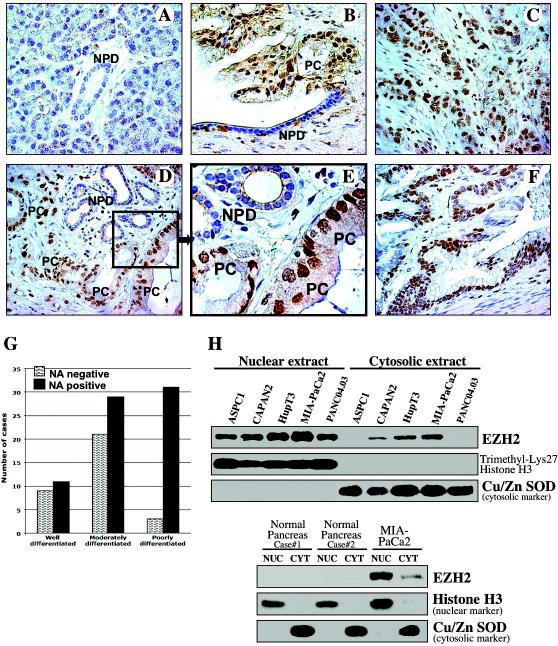
Figure 1. EZH2 is overexpressed and accumulated in the nucleus of pancreatic cancer cells.
(A-F) Immunohistochemical analysis of EZH2 expression and localization in (A) normal human pancreas and (B-F) pancreatic adenocarcinoma specimens. A, normal pancreatic duct (NPD) is indicated. B, Malignant pancreatic duct shows nuclear accumulation of EZH2, whereas adjacent normal pancreatic ductal cells show no nuclear EZH2 staining. Pancreatic cancer cells (PC). C, EZH2 nuclear accumulation in a poorly differentiated pancreatic adenocarcinoma. D, Nuclear accumulation of EZH2 found in cancer cells of moderately differentiated pancreatic adenocarcinoma but not in adjacent normal pancreatic ductal cells. E, Higher magnification of the delineated inset of (D) image. F, Nuclear accumulation of EZH2 in cancer cells of well differentiated pancreatic adenocarcinoma. G, Distribution of EZH2 staining patterns in pancreatic carcinomas. Nuclear accumulation (NA). H, Equivalent amounts (50 μg) of nuclear and cytosolic proteins isolated from the indicated pancreatic cancer cell lines and normal human pancreas tissue were separated by SDS-PAGE and immunoblotted.