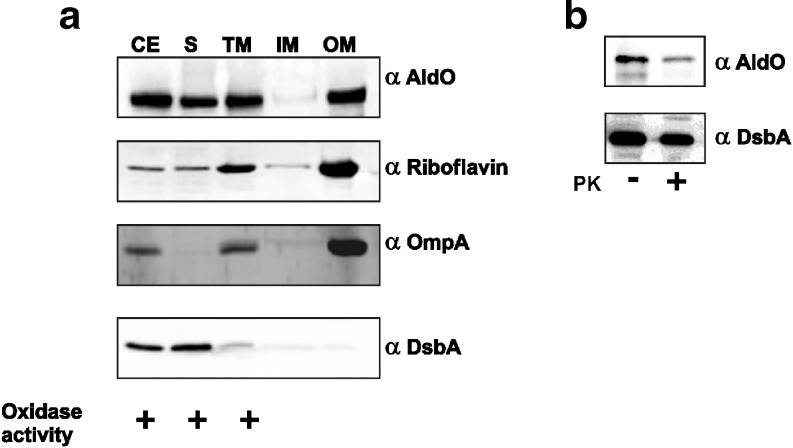
Fig. 3.
Subcellular localization of INP-AldO (a). E. coli cells expressing INP-AldO were fractionated into a cell extract (CE), soluble (S), and total membrane (TM) fraction. The total membrane fraction was further separated into an inner membrane (IM) and outer membrane (OM) fraction by extraction with 0.5% sarcosyl. Samples were normalized on the basis of OD660 and analyzed by immunoblotting with the indicated antisera. Oxidase activity in the cell extract, soluble, and total membrane fraction was determined using xylitol as substrate. Plus sign, oxidase activity; minus sign, no oxidase activity. b Protease accessibility analysis of surface displayed INP-AldO. E. coli cells expressing INP-AldO were treated (plus sign) or mock-treated (minus sign) with proteinase K (PK) to degrade cell surface proteins. Samples were normalized on the basis of OD660 and analyzed by immunoblotting with the indicated antisera