Abstract
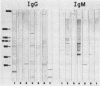
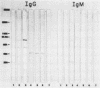
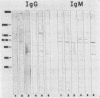
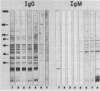
Sera of most adults have high agglutination test titers to Toxoplasma gondii whether or not the adults have other serological evidence of the infection. This finding has been attributed to the presence of naturally occurring antibodies to T. gondii. Consistent with this observation, we have recently noted that protein blots (PB) of sera of individuals not previously infected with T. gondii had immunoglobulin G (IgG) and IgM antibodies to antigens of the parasite. To further define the antigens recognized by these naturally occurring antibodies, we studied PB of sera of 44 adults and 9 children who had no serological evidence of the infection. Multiple antigens of T. gondii with molecular weights of 15,000 to greater than 205,000 were recognized by IgG and IgM natural antibodies of each of the sera. Although a relatively consistent pattern was noted on the IgM PB of the sera of the adults in the molecular weight range of 48,000 to 85,000, greater heterogeneity was noted on the IgG PB. The most common bands noted on the latter were of approximately 30,000 and 92,000 molecular weight. All of the PB obtained with the serial sera collected at yearly intervals from the children revealed bands; in some cases, new bands had appeared with time, and in others the pattern was constant. In children older than 8 years, the patterns of the PB were similar to those noted in PB of sera of the adults.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- AWAD F. I., LAINSON R. A note on the serology of sarcosporidiosis and toxoplasmosis. J Clin Pathol. 1954 May;7(2):152–156. doi: 10.1136/jcp.7.2.152. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Araujo F. G., Dubey J. P., Remington J. S. Antigenic similarity between the coccidian parasites Toxoplasma gondii and Hammondia hammondi. J Protozool. 1984 Feb;31(1):145–147. doi: 10.1111/j.1550-7408.1984.tb04304.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Desmonts G., Baufine-Ducrocq H., Couzineau P., Peloux Y. Anticorps toxoplasmiques naturels. Nouv Presse Med. 1974 Jun 15;3(24):1547–1549. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dubremetz J. F., Rodriguez C., Ferreira E. Toxoplasma gondii: redistribution of monoclonal antibodies on tachyzoites during host cell invasion. Exp Parasitol. 1985 Feb;59(1):24–32. doi: 10.1016/0014-4894(85)90053-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dzbenski T. H., Michalak T., Plonka W. S. Electron microscopic and radioisotopic studies on cap formation in Toxoplasma gondii. Infect Immun. 1976 Nov;14(5):1196–1201. doi: 10.1128/iai.14.5.1196-1201.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dzbeński T. H., Zielińska E. Antibody-induced formation of caps in Toxoplasma gondii. Experientia. 1976 Apr 15;32(4):454–456. doi: 10.1007/BF01920792. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FULTON J. D., TURK J. L. Direct agglutination test for Toxoplasma gondii. Lancet. 1959 Dec 12;2(7111):1068–1069. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(59)91535-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Franco E. L., Sulzer A. J., Higby R. W., Peralta J. M. Immunoglobulin G and immunoglobulin M polar staining of Toxoplasma gondii in the indirect immunofluorescence test. J Clin Microbiol. 1980 Dec;12(6):780–784. doi: 10.1128/jcm.12.6.780-784.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Handman E., Goding J. W., Remington J. S. Detection and characterization of membrane antigens of Toxoplasma gondii. J Immunol. 1980 Jun;124(6):2578–2583. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Handman E., Remington J. S. Serological and immunochemical characterization of monoclonal antibodies to Toxoplasma gondii. Immunology. 1980 Aug;40(4):579–588. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hobbs K. M., Sole E., Bettelheim K. A. Investigation into the immunoglobulin class responsible for the polar staining of Toxoplasma gondii in the fluorescent antibody test. Zentralbl Bakteriol Orig A. 1977 Nov;239(3):409–413. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hyde B., Barnett E. V., Remington J. S. Method for differentiation of nonspecific from specfic toxoplasma IgM fluorescent antibodies in patients with rheumatoid factor. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1975 Apr;148(4):1184–1188. doi: 10.3181/00379727-148-38713. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- JACOBS L. TOXOPLASMA AND TOXOPLASMOSIS. Annu Rev Microbiol. 1963;17:429–450. doi: 10.1146/annurev.mi.17.100163.002241. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kasper L. H., Crabb J. H., Pfefferkorn E. R. Purification of a major membrane protein of Toxoplasma gondii by immunoabsorption with a monoclonal antibody. J Immunol. 1983 May;130(5):2407–2412. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LUNDE M. N., JACOBS L. ANTIGENIC RELATIONSHIP OF TOXOPLASMA GONDII AND BESNOITIA JELLISONI. J Parasitol. 1965 Apr;51:273–276. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Naot Y., Remington J. S. An enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay for detection of IgM antibodies to Toxoplasma gondii: use for diagnosis of acute acquired toxoplasmosis. J Infect Dis. 1980 Nov;142(5):757–766. doi: 10.1093/infdis/142.5.757. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sabin A. B., Feldman H. A. Dyes as Microchemical Indicators of a New Immunity Phenomenon Affecting a Protozoon Parasite (Toxoplasma). Science. 1948 Dec 10;108(2815):660–663. doi: 10.1126/science.108.2815.660. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Santoro F., Afchain D., Pierce R., Cesbron J. Y., Ovlaque G., Capron A. Serodiagnosis of toxoplasma infection using a purified parasite protein (P30). Clin Exp Immunol. 1985 Nov;62(2):262–269. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sharma S. D., Mullenax J., Araujo F. G., Erlich H. A., Remington J. S. Western Blot analysis of the antigens of Toxoplasma gondii recognized by human IgM and IgG antibodies. J Immunol. 1983 Aug;131(2):977–983. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Suggs M., Walls K. W., Kagan I. G. Comparative antigenic study of Besnoitia jellisoni, B. Panamenis and five Toxoplasma gondii isolates. J Immunol. 1968 Jul;101(1):166–175. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sulzer A. J., Hall E. C. Indirect fluorescent antibody tests for parasitic diseases. IV. Statistical study of variation in the indirect fluorescent antibody (IFA) test for toxoplasmosis. Am J Epidemiol. 1967 Sep;86(2):401–407. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.aje.a120750. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sulzer A. J., Wilson M., Hall E. C. Toxoplasma gondii: polar staining in fluorescent antibody test. Exp Parasitol. 1971 Apr;29(2):197–200. doi: 10.1016/0014-4894(71)90024-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Towbin H., Staehelin T., Gordon J. Electrophoretic transfer of proteins from polyacrylamide gels to nitrocellulose sheets: procedure and some applications. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Sep;76(9):4350–4354. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.9.4350. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walton B. C., Benchoff B. M., Brooks W. H. Comparison of the indirect fluorescent antibody test and methylene blue dye test for detection of antibodies to Toxoplasma gondii. Am J Trop Med Hyg. 1966 Mar;15(2):149–152. doi: 10.4269/ajtmh.1966.15.149. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van Renterghem L., van Nimmen L. Indirect immunofluorescence in toxoplasmosis: frequency, nature and specificity of polar staining. Zentralbl Bakteriol Orig A. 1976 Aug;235(4):559–565. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]