Abstract
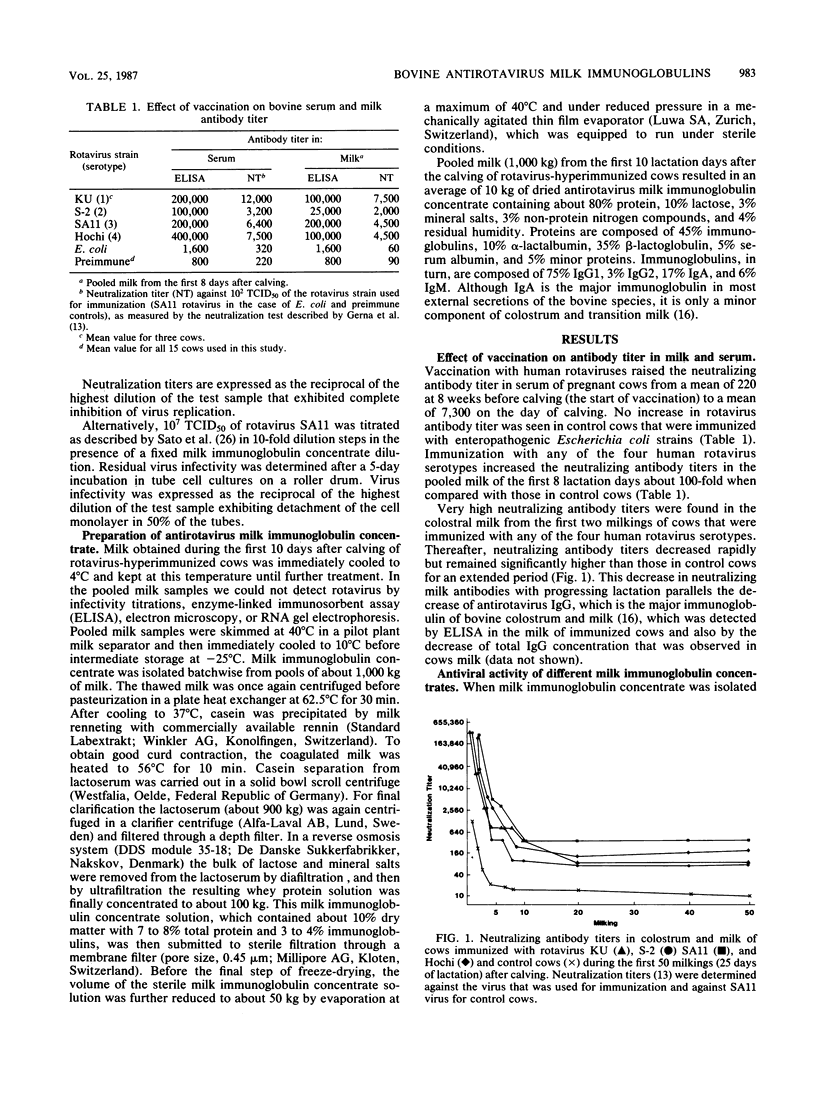
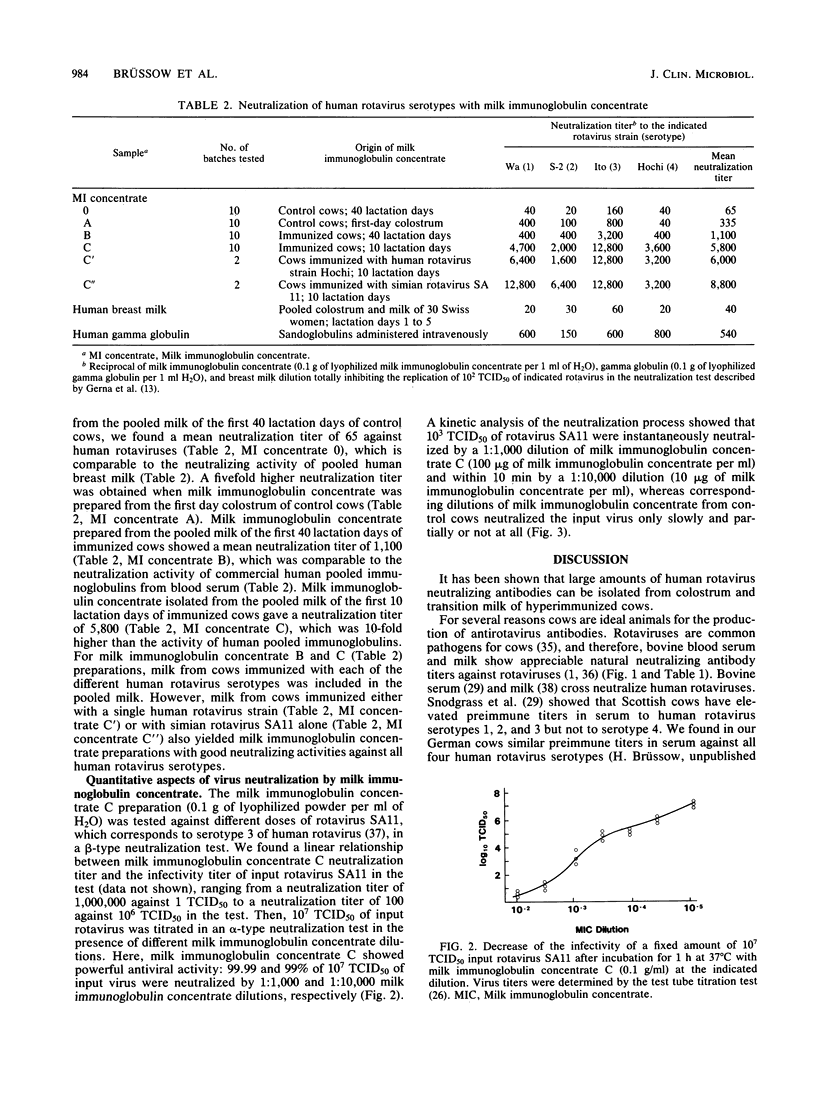
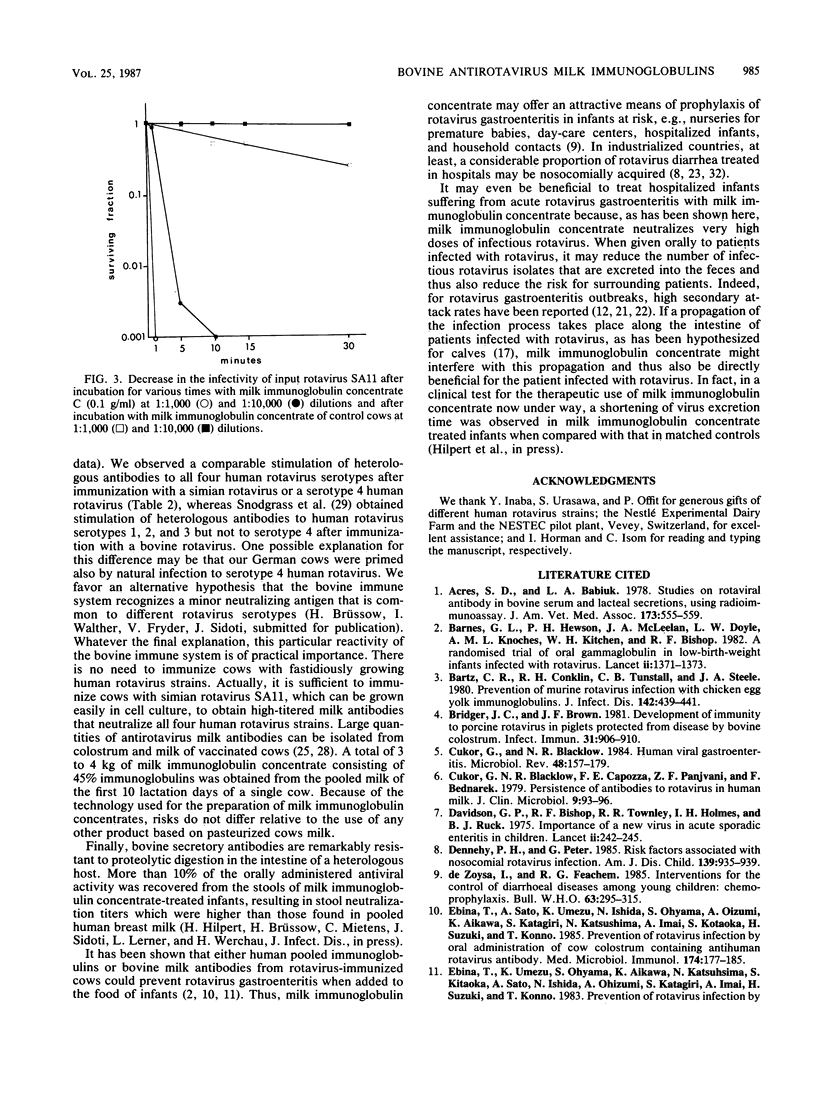
Pregnant cows were successfully hyperimmunized with all four human rotavirus serotypes, resulting in a 100-fold increase in neutralizing milk antibody titers over those of controls. Milk antibodies were isolated batchwise from 1,000 kg of pooled milk for the first 10 lactation days, yielding 10 kg of freeze-dried milk immunoglobulin concentrate consisting of 50% bovine milk immunoglobulins. Milk immunoglobulin concentrate showed neutralizing activities against all four human rotavirus serotypes that were 100 times higher than those in pooled human milk samples and 10 times higher than those in a commercial pooled immunoglobulin preparation from pooled human blood serum. In vitro neutralization tests showed that milk immunoglobulin concentrate had powerful antiviral activity, even against very high doses of infectious rotaviruses. Because the technology of the milk immunoglobulin concentrate ensures that it is innocuous and can be used for oral application, it is proposed that milk immunoglobulin concentrate be used to induce passive immunity to infantile rotavirus gastroenteritis.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Acres S. D., Babiuk L. A. Studies on rotaviral antibody in bovine serum and lacteal secretions, using radioimmunoassay. J Am Vet Med Assoc. 1978 Sep 1;173(5 Pt 2):555–559. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barnes G. L., Doyle L. W., Hewson P. H., Knoches A. M., McLellan J. A., Kitchen W. H., Bishop R. F. A randomised trial of oral gammaglobulin in low-birth-weight infants infected with rotavirus. Lancet. 1982 Jun 19;1(8286):1371–1373. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(82)92496-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bartz C. R., Conklin R. H., Tunstall C. B., Steele J. H. Prevention of murine rotavirus infection with chicken egg yolk immunoglobulins. J Infect Dis. 1980 Sep;142(3):439–441. doi: 10.1093/infdis/142.3.439. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bridger J. C., Brown J. F. Development of immunity to porcine rotavirus in piglets protected from disease by bovine colostrum. Infect Immun. 1981 Mar;31(3):906–910. doi: 10.1128/iai.31.3.906-910.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cukor G., Blacklow N. R., Capozza F. E., Panjvani Z. F., Bednarek F. Persistence of antibodies to rotavirus in human milk. J Clin Microbiol. 1979 Jan;9(1):93–96. doi: 10.1128/jcm.9.1.93-96.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cukor G., Blacklow N. R. Human viral gastroenteritis. Microbiol Rev. 1984 Jun;48(2):157–179. doi: 10.1128/mr.48.2.157-179.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davidson G. P., Bishop R. F., Townley R. R., Holmes I. H. Importance of a new virus in acute sporadic enteritis in children. Lancet. 1975 Feb 1;1(7901):242–246. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(75)91140-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dennehy P. H., Peter G. Risk factors associated with nosocomial rotavirus infection. Am J Dis Child. 1985 Sep;139(9):935–939. doi: 10.1001/archpedi.1985.02140110089037. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ebina T., Sato A., Umezu K., Ishida N., Ohyama S., Oizumi A., Aikawa K., Katagiri S., Katsushima N., Imai A. Prevention of rotavirus infection by oral administration of cow colostrum containing antihumanrotavirus antibody. Med Microbiol Immunol. 1985;174(4):177–185. doi: 10.1007/BF02123694. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fonteyne J., Zissis G., Lambert J. P. Recurrent rotavirus gastroenteritis. Lancet. 1978 May 6;1(8071):983–983. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(78)90263-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gerna G., Battaglia M., Milenesi G., Passarani N., Percivalle E., Cattaneo E. Serotyping of cell culture-adapted subgroup 2 human rotavirus strains by neutralization. Infect Immun. 1984 Feb;43(2):722–729. doi: 10.1128/iai.43.2.722-729.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kapikian A. Z., Kim H. W., Wyatt R. G., Cline W. L., Arrobio J. O., Brandt C. D., Rodriguez W. J., Sack D. A., Chanock R. M., Parrott R. H. Human reovirus-like agent as the major pathogen associated with "winter" gastroenteritis in hospitalized infants and young children. N Engl J Med. 1976 Apr 29;294(18):965–972. doi: 10.1056/NEJM197604292941801. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mach J. P., Pahud J. J. Secretory IgA, a major immunoglobulin in most bovine external secretions. J Immunol. 1971 Feb;106(2):552–563. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Middleton P. J., Szymanski M. T., Petric M. Viruses associated with acute gastroenteritis in young children. Am J Dis Child. 1977 Jul;131(7):733–737. doi: 10.1001/archpedi.1977.02120200015004. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Offit P. A., Clark H. F. Protection against rotavirus-induced gastroenteritis in a murine model by passively acquired gastrointestinal but not circulating antibodies. J Virol. 1985 Apr;54(1):58–64. doi: 10.1128/jvi.54.1.58-64.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pickering L. K., Evans D. G., DuPont H. L., Vollet J. J., 3rd, Evans D. J., Jr Diarrhea caused by Shigella, rotavirus, and Giardia in day-care centers: prospective study. J Pediatr. 1981 Jul;99(1):51–56. doi: 10.1016/s0022-3476(81)80956-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rodriguez W. J., Kim H. W., Brandt C. D., Yolken R. H., Richard M., Arrobio J. O., Schwartz R. H., Kapikian A. Z., Chanock R. M., Parrott R. H. Common exposure outbreak of gastroenteritis due to type 2 rotavirus with high secondary attack rate within families. J Infect Dis. 1979 Sep;140(3):353–357. doi: 10.1093/infdis/140.3.353. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ryder R. W., McGowan J. E., Hatch M. H., Palmer E. L. Reovirus-like agent as a cause of nosocomial diarrhea in infants. J Pediatr. 1977 May;90(5):698–702. doi: 10.1016/s0022-3476(77)81230-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saif L. J., Redman D. R., Smith K. L., Theil K. W. Passive immunity to bovine rotavirus in newborn calves fed colostrum supplements from immunized or nonimmunized cows. Infect Immun. 1983 Sep;41(3):1118–1131. doi: 10.1128/iai.41.3.1118-1131.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saif L. J., Smith K. L., Landmeier B. J., Bohl E. H., Theil K. W., Todhunter D. A. Immune response of pregnant cows to bovine rotavirus immunization. Am J Vet Res. 1984 Jan;45(1):49–58. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sato K., Inaba Y., Miura Y., Tokuhisa S., Matumoto M. Antigenic relationships between rotaviruses from different species as studied by neutralization and immunofluorescence. Arch Virol. 1982;73(1):45–50. doi: 10.1007/BF01341726. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sheridan J. F., Smith C. C., Manak M. M., Aurelian L. Prevention of rotavirus-induced diarrhea in neonatal mice born to dams immunized with empty capsids of simian rotavirus SA-11. J Infect Dis. 1984 Mar;149(3):434–438. doi: 10.1093/infdis/149.3.434. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Snodgrass D. R., Fahey K. J., Wells P. W., Campbell I., Whitelaw A. Passive immunity in calf rotavirus infections: maternal vaccination increases and prolongs immunoglobulin G1 antibody secretion in milk. Infect Immun. 1980 May;28(2):344–349. doi: 10.1128/iai.28.2.344-349.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Snodgrass D. R., Ojeh C. K., Campbell I., Herring A. J. Bovine rotavirus serotypes and their significance for immunization. J Clin Microbiol. 1984 Sep;20(3):342–346. doi: 10.1128/jcm.20.3.342-346.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Snodgrass D. R., Wells P. W. Passive immunity in rotaviral infections. J Am Vet Med Assoc. 1978 Sep 1;173(5 Pt 2):565–568. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Snodgrass D. R., Wells P. W. Rotavirus infection in lambs: studies on passive protection. Arch Virol. 1976;52(3):201–205. doi: 10.1007/BF01348017. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tufvesson B., Johnsson T. Occurrence of reo-like calf viruses in young children with acute gastroenteritis. Diagnoses established by electron microscopy and complement fixation, using the reo-like virus as antigen. Acta Pathol Microbiol Scand B. 1976 Feb;84(1):22–28. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Urasawa S., Urasawa T., Taniguchi K. Three human rotavirus serotypes demonstrated by plaque neutralization of isolated strains. Infect Immun. 1982 Nov;38(2):781–784. doi: 10.1128/iai.38.2.781-784.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vesikari T., Isolauri E., Delem A., d'Hondt E., André F. E., Beards G. M., Flewett T. H. Clinical efficacy of the RIT 4237 live attenuated bovine rotavirus vaccine in infants vaccinated before a rotavirus epidemic. J Pediatr. 1985 Aug;107(2):189–194. doi: 10.1016/s0022-3476(85)80123-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Woode G. N., Bridger J. C. Viral enteritis of calves. Vet Rec. 1975 Jan 25;96(4):85–88. doi: 10.1136/vr.96.4.85. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Woode G. N., Jones J., Bridger J. Levels of colostral antibodies against neonatal calf diaahoea virus. Vet Rec. 1975 Aug 23;97(8):148–149. doi: 10.1136/vr.97.8.148. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wyatt R. G., Greenberg H. B., James W. D., Pittman A. L., Kalica A. R., Flores J., Chanock R. M., Kapikian A. Z. Definition of human rotavirus serotypes by plaque reduction assay. Infect Immun. 1982 Jul;37(1):110–115. doi: 10.1128/iai.37.1.110-115.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yolken R. H., Losonsky G. A., Vonderfecht S., Leister F., Wee S. B. Antibody to human rotavirus in cow's milk. N Engl J Med. 1985 Mar 7;312(10):605–610. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198503073121002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- de Zoysa I., Feachem R. G. Interventions for the control of diarrhoeal diseases among young children: chemoprophylaxis. Bull World Health Organ. 1985;63(2):295–315. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


