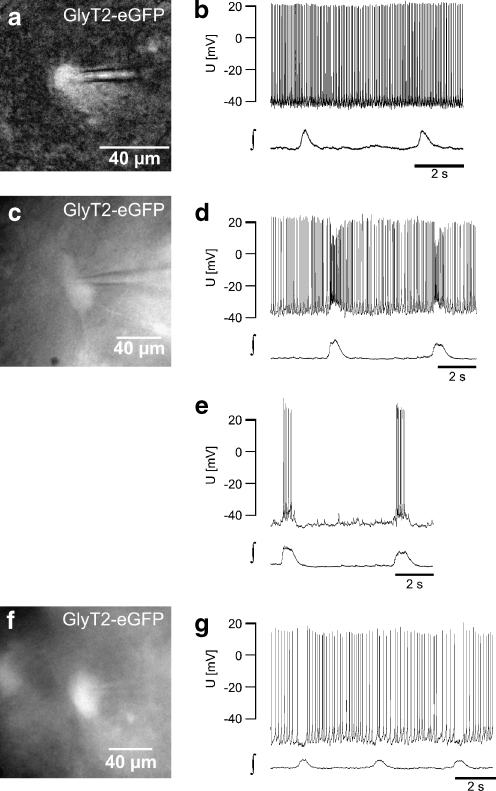
Fig. 4.
a CCD camera image of the EGFP-expression of a glycinergic neuron recorded in b (epifluorescence, excitation using 467 nm). b Current clamp recording of the glycinergic neuron (in a) showing tonic spike activity without rhythmic modulation (∫ integral of the population field potential). c–e Example of a glycinergic neuron (c) that receives phasic excitatory input. d Current clamp recording showing tonic activity with a phasic increase of action potential frequency. e Injection of negative current (−40 pA) results in a cessation of tonic activity and uncovers bursts of action potentials resulting from phasic excitation. f, g Glycinergic neuron (f) showing a phasic reduction of action potential frequency, the typical behavior of a tonic expiratory neuron (g)