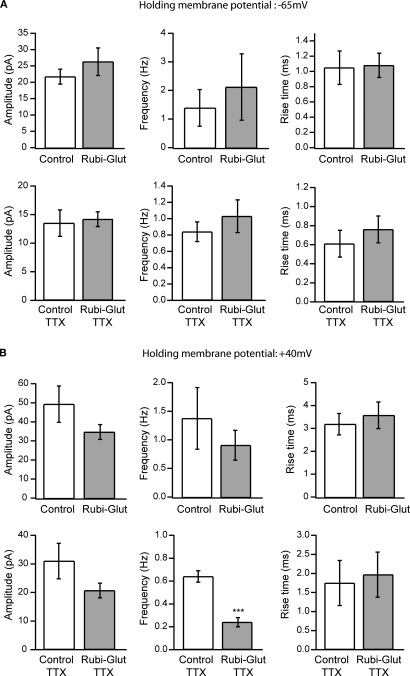
Figure 2.
Effect of RuBi-Glutamate on spontaneous synaptic currents. (A) Effects of RuBi-Glutamate on spontaneous activity recorded at a holding membrane potential of −65 mV. At this resting potential, RuBi-Glutamate (300 μM) had no significant effect on the average amplitude, frequency or rise time of spontaneous PSCs (n = 6 neurons) or of miniature PSCs recorded in the presence of TTX (n = 6 neurons). (B) Effects of RuBi-Glutamate on spontaneous activity recorded at +40 mV. RuBi-Glutamate (300 μM) tends to reduce the amplitude and frequency of spontaneous and miniature PSCs, but only the reduction of frequency of miniature PSCs is statistically significant (p < 0.001, n = 6 neurons). There was no change in the rise time of the events. Because both excitatory and inhibitory events are recorded at +40 mV, this indicates that RuBi-Glutamate may have an inhibitory effect on IPSCs. Error bars represent SEM. ***p < 0.001.