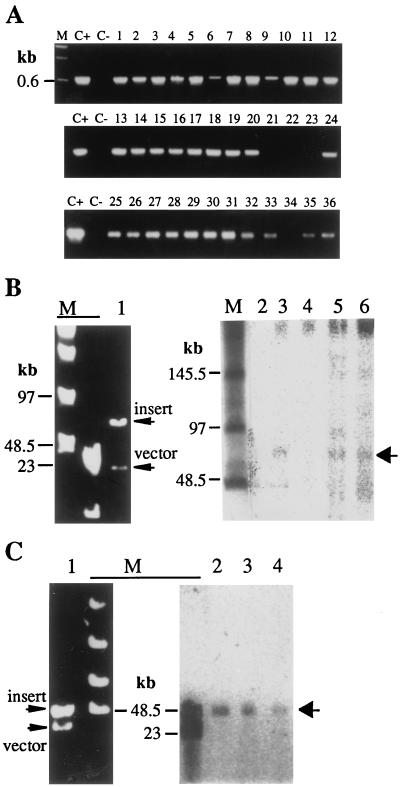
Figure 3.
Transgenes in Arabidopsis plants transformed with TAC clones. (A) A. thaliana ecotype WS was transformed with TAC clones carrying either 40-kb (lanes 1–20) or 80-kb (lanes 21–36) genomic DNA fragments of ecotype Columbia. The sacB gene of 36 transgenic plants (hygromycin-resistant plants) was checked by PCR (Fig. 1). C+ and C−, positive (a TAC clone) and negative (untransformed plant) controls, respectively. (B) Transgenic lines transformed with a 75-kb TAC clone was self-crossed, and then the resulting T2 plants were analyzed by genomic Southern experiments. Genomic DNAs of transgenic and untransformed (negative control) plants were digested with I-SceI and hybridized with a HPT gene probe. The hybridized bands (lanes 3, 5, and 6) are shown by the arrow on the right. No hybridization band corresponding to the I-SceI fragment is seen in lanes 2 and 4. Lane 1, plasmid DNA digested with I-SceI; lanes 2–6, genomic Southern blotting of DNAs from untransformed plants (lane 2) and T2 lines (lanes 3–6). (C) The progenies of a transgenic line transformed with a 45-kb TAC clone were analyzed. Genomic DNAs of a T2 line (lane 2) and its T3 progenies (lanes 3 and 4) were digested with I-SceI and hybridized with the HPT gene probe. Lane 1, plasmid DNA digested with I-SceI; lanes 2–4, genomic Southern blotting of DNA digested with I-SceI.