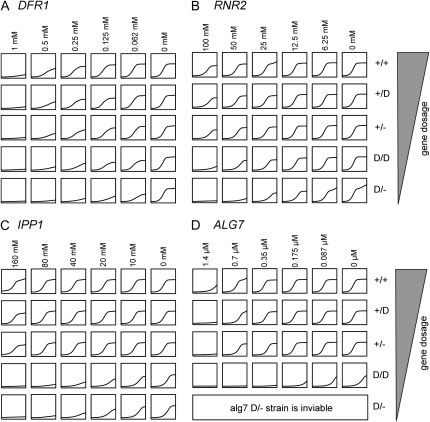
Figure 1.—
Drug sensitivity of gene-dose strains. Each column represents a different drug concentration with concentration indicated at the top. Each row represents a different gene-dose strain with the strain genotype indicated at the right. (A) Growth curve of different DFR1 gene-dose strains. Each strain was grown in YPD medium with or without methotrexate. (B) Growth curve of different RNR2 gene-dose strains. Each strain was grown in YPD medium with or without hydroxyurea. (C) Growth curve of different IPP1 gene-dose strains. Each strain was grown in YPD medium with or without NaF. (D) Growth curve of different ALG7 gene-dose strains. Each strain was grown in YPD medium with or without tunicamycin. Strains and genotypes are listed in Table S1. The diploid parental wild-type strain is BY4743. All DAmP and heterozygous strains were created as described (Giaever et al. 2002; Schuldiner et al. 2005). Primers used to create gene-dose strains are listed in Table S2. Each primer contains 40 bases of homology to its target gene and 18 bases of homology to the KanMX4 or NatMX4 cassette. To create double DAmP strains, two haploid DAmP strains were created, one with the 3′-UTR disrupted using a KanMX4 cassette in strain BY4741 and the other with a NatMX4 cassette in strain BY4742. Haploid DAmP strains were mated and diploids selected on YPD medium containing 250 mg/liter of G418 (AgriBio, no. 3000) and 100 mg/liter of nourseothricin (Werner Bioagents). The hemizygous DAmP strains (D/− allele) were constructed by inserting the NatMX4 cassette immediately after the stop codon of the gene of interest in a heterozygous strain and were selected on YPD medium containing 250 mg/liter of G418 and 100 mg/liter of nourseothricin.