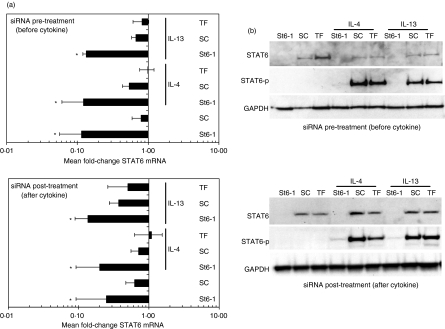
Figure 3.
RNA interference (RNAi) of signal transducer and activator of transcription 6 (STAT6) is undiminished in the presence of STAT6-activating cytokines. A549 cells were either pretreated or post-treated with St6-1 small interfering RNA (siRNA) relative to stimulation with cytokine [interleukin (IL)-4 or IL-13; 50 ng/ml] and STAT6 expression was analysed at the mRNA and protein levels by real-time reverse transcription–polymerase chain reaction (RT-PCR) (a) and western blotting (b), respectively. (a) Irrespective of the timing of cytokine addition, St6-1 siRNA treatment induced a significant down-regulation of STAT6 mRNA compared with scrambled control (SC) siRNA-treated cultures (*P ≤ 0·05). The fold-change in STAT6 mRNA expression was similar in siRNA pretreatment versus siRNA post-treatment cultures. (b) Representative western blots showing absence of detectable STAT6 protein expression in cultures either pretreated with St6-1 siRNA (48 hr prior to cytokine stimulation) or post-treated with St6-1 siRNA (24 hr after cytokine stimulation). Phosphorylated STAT6 (STAT6-p) was undetectable in St6-1 siRNA-treated cultures.