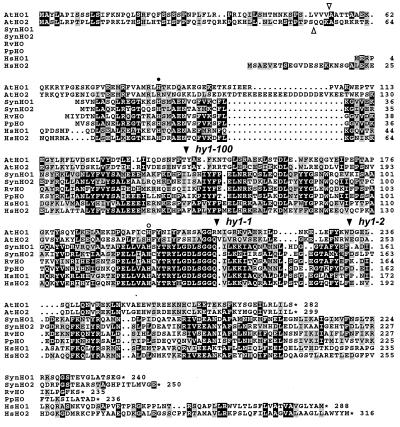
Figure 4.
Amino acid sequence comparison of AtHO1 and AtHO2 with HOs from cyanobacteria, alga, and humans. The alignment was created by using macboxshade 2.7 (Institute for Animal Health, Pirbright Surrey, U.K.). Identical and similar residues are in reverse type or shaded boxes, respectively. The open triangles identify the predicted cleavage sites for the transit peptide of AtHO1 and AtHO2, and the solid triangles denote the sites altered in the hy1–1, hy1–100, and hy1–2 mutants. The closed and open circles mark the His residues important in animal HOs for heme binding and protein structure, respectively. Numbers at the right indicate the respective amino acid residues. Asterisks identify the positions of stop codons. Sequences include Synechocystis (Syn) HO1 (D90091) and HO2 (D90912), Rhodella violacea (Rv) HO1 (AF000717), Porphyra purpurea (Pp) HO (P51271), and human (Hs) HO1 (P09601) and HO2 (P30519).