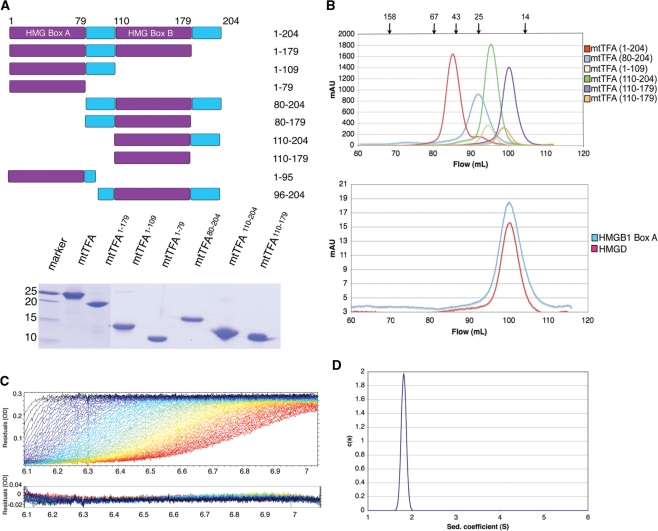
Figure 1.
Human mtTFA is an asymmetric monomer in the absence of DNA. (A) Deletion constructs of h-mtTFA. The upper panel shows a schematic diagram and the lower panel shows SDS–PAGE of h-mtTFA deletion constructs on a 15% polyacrylamide gel. (B) Size-exclusion chromatography (Superdex 200; GE Healthcare) elution profiles of h-mtTFA and h-mtTFA deletion constructs, mtTFA1–179, mtTFA1–109, mtTFA1–79, mtTFA80–204, mtTFA110–204 and mtTFA110–179 (top panel), and the single HMG domains, HMGB1 box A and HMGD (lower panel) in 50 mM HEPES–Na pH 7.0, 150 mM NaCl, 1 mM EDTA and 1 mM DTT. The position of each size standard is indicated by arrows above the top panel for amylase (158 kDa), bovine serum albumin (67 kDa), ovalbumin (43 kDa), chymotrypsinogen A (25 kDa) and RNase A (14 kDa). The void volume was at 45 ml and is not shown. (C) Sedimentation velocity profiles for the raw data acquired at different time points and the residuals after fittings had been performed using SEDFIT in 50 mM HEPES–Na pH 7.0, 150 mM NaCl, 1 mM EDTA and 1 mM DTT. (D) Calculated sedimentation coefficient distributions for the full-length h-mtTFA.