Fig. 1.
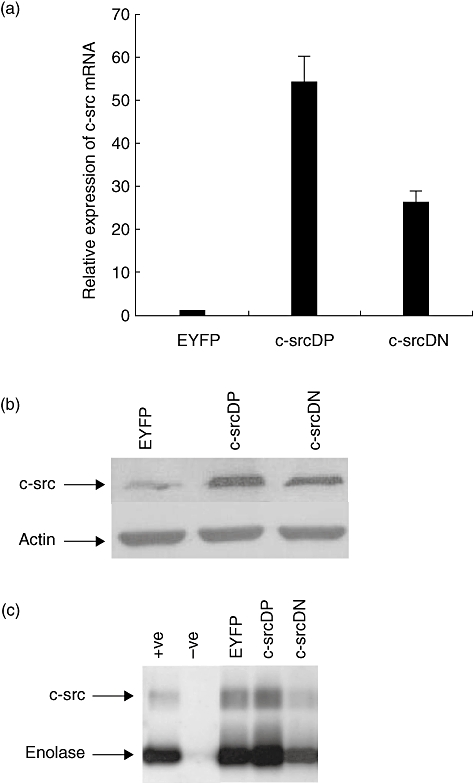
c-Src expression in transduced human B lymphocytes. Normal human B lymphocytes were infected with recombinant adenovirus encoding enhanced yellow fluorescent protein (EYFP), c-src dominant-positive (DP) or c-src dominant-negative (DN) and cultured in the CD40/CD154 system. Expression of c-Src was analysed 48 h post-infection. (a) c-src mRNA levels were determined by quantitative competitive–polymerase chain reaction (Q–PCR). Fold expression of the transcripts was expressed relative to transcripts level in Ad5/F35-EYFP-infected B lymphocytes. All data represent the means of three independent experiments; standard deviations are indicated. (b) c-Src protein levels were determined by Western blot analysis with anti-c-Src clone GD11 as described in Materials and methods. Actin staining was used as loading control. (c) c-Src kinase activity in transduced human B lymphocytes (3 × 106 cell equivalents per lane) was performed as described in Materials and methods. 32P-labelled proteins were visualized by autoradiography. Recombinant human c-Src was used as positive control (+ve) and antibody coated beads without lysate was the negative control (−ve). Arrows indicate the position of autophosphorylated c-Src and tyrosine phosphorylated enolase.
