Fig. 4.
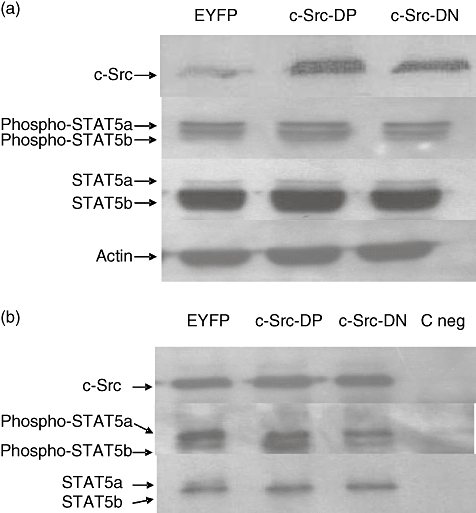
c-Src and signal transducer and activator of transcription 5b (STAT5b) association in human B lymphocytes. Normal human B lymphocytes were infected with recombinant adenovirus encoding enhanced yellow fluorescent protein (EYFP), c-src dominant-positive (DP) or c-src dominant-negative (DN) and cultured in the CD40/CD154 system. Cell pellets were collected 48 h post-infection and lysed in radioimmunoprecipitation assay (RIPA) lysis buffer. (a) c-Src and STAT5b protein levels were determined by Western blot analysis with anti-Src, anti-Stat5a/b and anti-phosphoStat5a/b antibodies. Actin staining was used as loading control. Representative result of one experiment of four are shown. (b) Proteins from 5 × 106 cell equivalents were immunoprecipitated using anti-c-Src (monoclonal antibody 327) bound to rabbit anti-mouse immunoglobulin (Ig)G-protein A Sepharose. Immunoprecipitates were analysed by Western blot with anti-c-Src, anti-Stat5a/b and anti-phosphoStat5a/b antibodies. Coated beads with an anti-SV40 large T antigen was used as negative control (C neg). Representative result of one experiment of three are shown.
