Fig. 3.
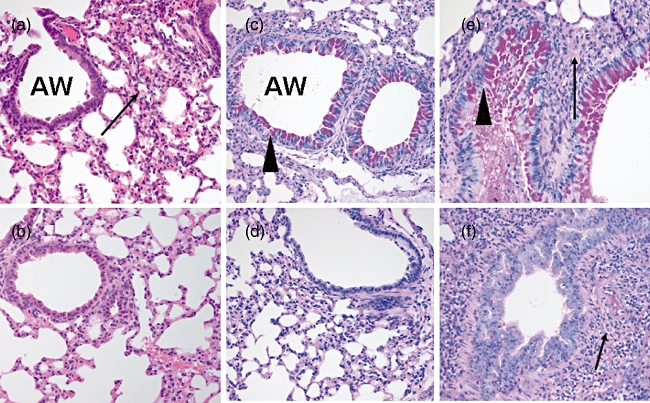
Lung tissues stained with haematoxylin and eosin and examined by light microscopy (a,b). (a) The ovalbumin (OVA)-sensitized/challenged mice exhibited marked infiltration of eosinophils and other inflammatory cells (arrows) in the interstitium of the lungs. The airways were surrounded by dense cellular infiltrate. (b) The control mice had airways of normal appearance. Inflammatory cell infiltration was absent in the lung interstitium. The lung tissues were stained with periodic acid Schiff and examined by light microscopy (c–f). (c) Airway goblet cell hyperplasia and mucin hypersecretion (arrowheads) were observed in OVA-sensitized/challenged mice. (d) Airway mucin was scant in the control mice. (e) Alveolar consolidation (arrow) and mucin hypersecretion (arrowhead) were observed in the OVA-sensitized/challenged mice with pneumococcal pneumonia. (f) Only alveolar consolidation (arrow) was observed and airway mucin was scant in the control mice with pneumococcal pneumonia.
