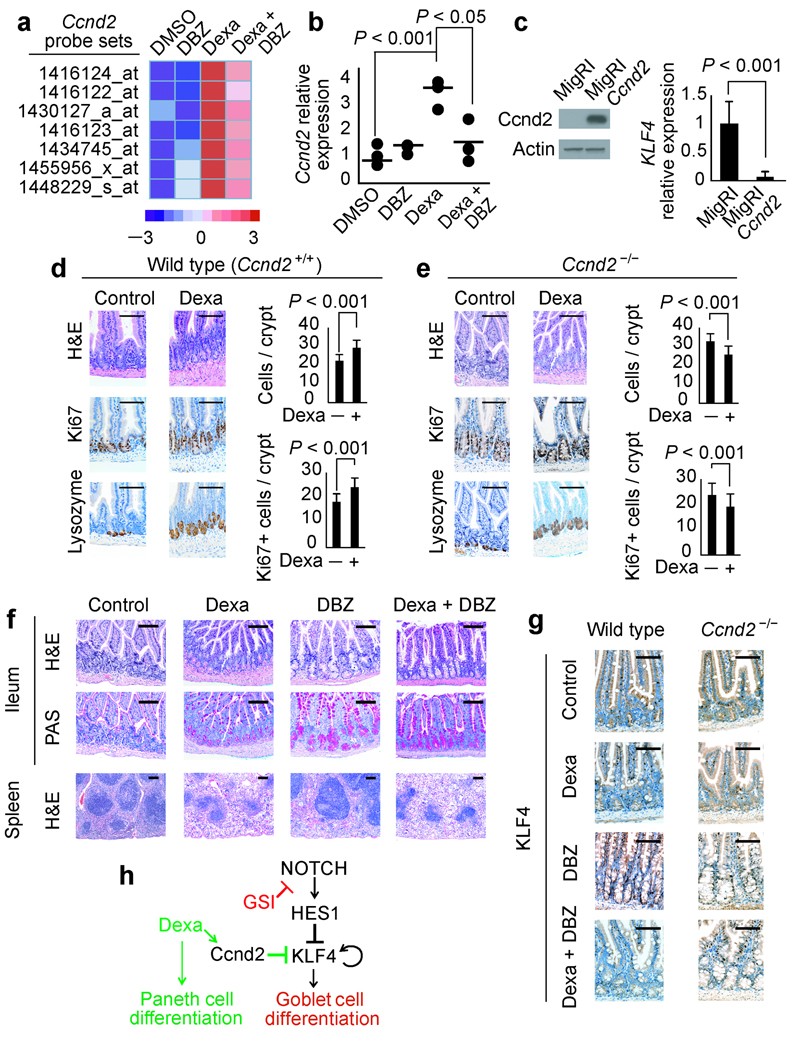
Figure 6.
Glucocorticoid-induced Cnnd2 upregulation mediates the enteroprotective effect of dexamethasone against GSI-induced gut toxicity. (a) Microarray analysis of Ccnd2 transcript levels in the small intestine of mice treated with vehicle (DMSO), DBZ, dexamethasone (Dexa) and dexamethasone plus DBZ (Dexa + DBZ) for 5 days. The heat map diagram shows average values from duplicate samples. (b) Quantitative RT-PCR analysis of the Ccnd2 gene in the small intestine of mice treated with vehicle (DMSO), DBZ, dexamethasone (Dexa) and dexamethasone plus DBZ (Dexa + DBZ). Horizontal bars indicate the mean expression level in each group. (c) Retroviral expression of Ccnd2 in AGS cells induces transcriptional downregulation of KLF4. (d, e) Histological and histochemical analysis of small intestines from wild type (d) and Ccnd2−/− mice (e) treated with vehicle only (Control) or dexamethasone (Dexa). (f) Histological and histochemical studies of small intestines and spleens from Ccnd2−/− mice treated with vehicle only (DMSO), dexamethasone, DBZ and dexamethasone plus DBZ for 10 days. H&E: haemotoxylin and eosin staining. Scale bars represent 100 µm. (g) Immunohistochemistry analysis of Klf4 expression in small intestine of wild type and Ccnd2−/− mice treated with dexamethasone, DBZ or the combination of dexamethasone plus DBZ for 5 days. Scale bars represent 100 µm. (h) Schematic representation of the transcriptional regulatory network controlling cell differentiation in the intestinal cells downstream of Notch and glucocorticoid receptor signaling.