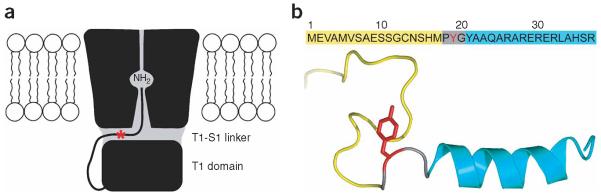
Figure 4.
A model for the N-type inactivation of Kv channels. (a) The model proposes that the N-terminal inactivation peptide snakes through the side portal, and then enters and plugs the inner pore of the Kv channel14,15. The side portals are formed by the transmembrane domain, the T1 domain and the T1-S1 linker. The hydrophobic region of the inactivation peptide reaches into the inner pore, and the positively charged residues in the hydrophilic region of the inactivation peptide make electrostatic interactions with negatively charged surfaces of the T1 domain and the T1-S1 linker. (b) The amino-acid sequences of the N-terminal inactivation peptide of Kv1.4, and its structure in aqueous solution determined by NMR28. Only one conformer of the random N-terminal Met1-Met17 is shown in yellow. The β-turn and α-helix are colored gray and cyan, respectively. Residue Tyr19 is colored red, and its approximate position is indicated with a red star in a.