Figure 1.
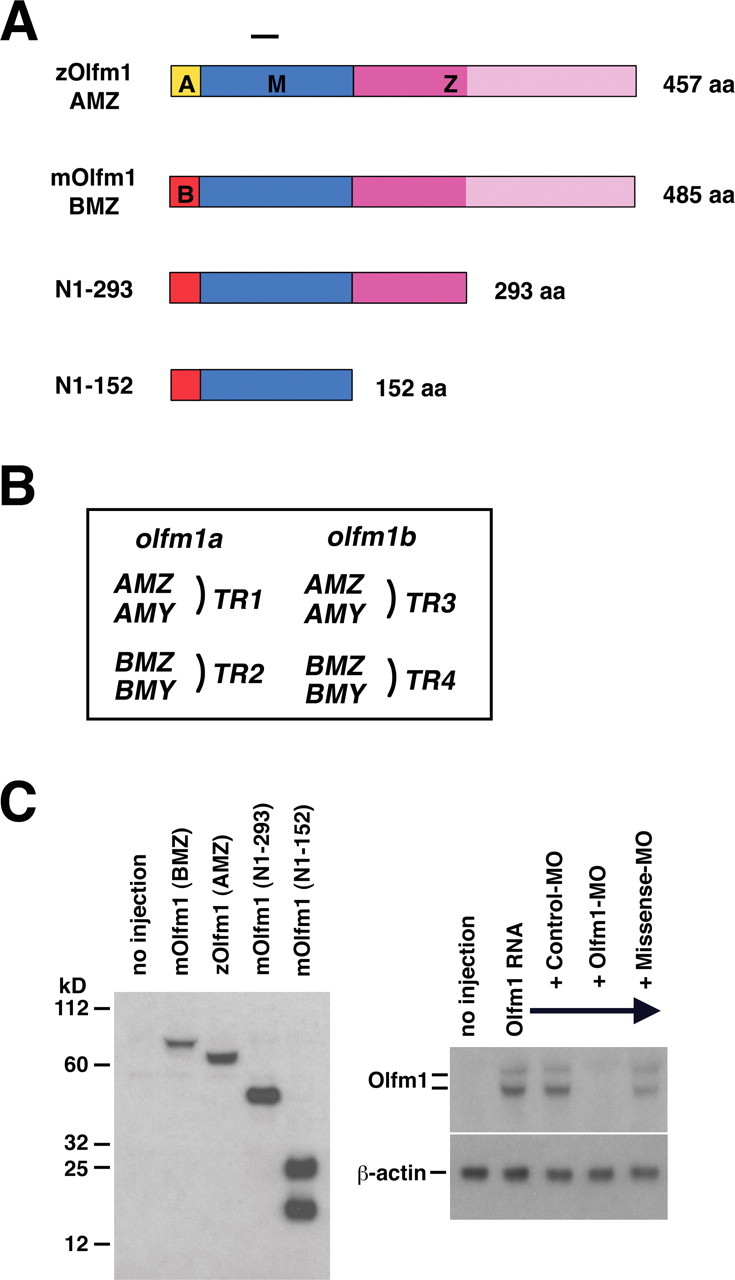
A, Schematic diagram of the Olfm1 constructs used in this study. A, M, and Z denote different protein regions. The A or B regions (shown in yellow or red, respectively) contain a signal peptide, the M region (shown in blue) is common between different Olfm1 forms, and the Z region (shown in dark and light pink) contains the olfactomedin domain (shown in light pink). B, The nomenclature of transcripts of zebrafish olfm1a and olfm1b genes. C, Expression of different Olfm1 forms 24 h after injection of 0.1 ng of corresponding RNAs at cell stage 1. Total soluble proteins were analyzed by Western blotting using the monoclonal antibody against the peptide in the M domain (left). The right demonstrates inhibition of Olfm1 by Olfm1–MO coinjection. Mouse Olfm1 RNA preceded by the zebrafish sequence sensitive to Olfm1–MO was synthesized and injected into cell soma of cell stage 1 embryos with or without an injection of the Olfm1–MO, control MO, and missense MO into the egg yolk. The Olfm1–MO completely inhibited the Olfm1 protein expression (appeared as upper glycosylated and lower unglycosylated bands) from the injected RNA in the bud stage embryos.
