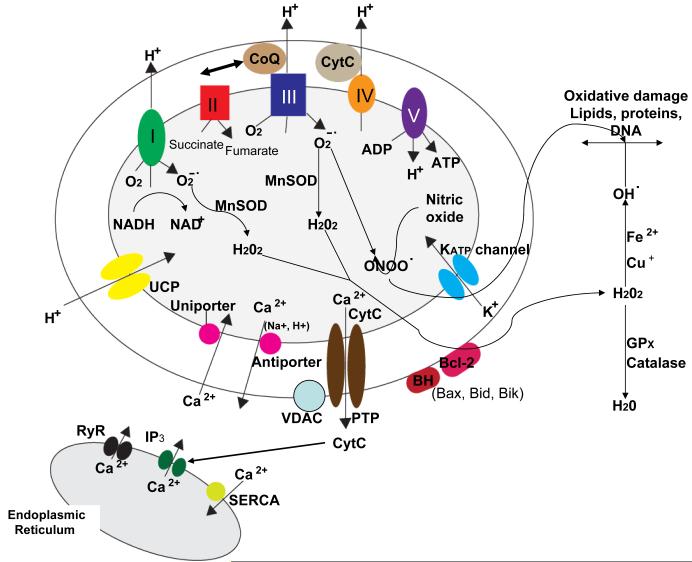
Figure 1.
Proteins involved in mitochondrial bioenergetics, oxygen radical metabolism and Ca2+ regulation. The electron transport chain consists of four protein complexes (I-IV) and the ATP synthase (complex V) located in the mitochondrial inner membrane. The activity of complex I converts NADH to NAD+ and the activity of complex II converts succinate to fumarate. Complexes I, III and IV transport protons (H+) across the membrane and complexes I and III generate superoxide anion radical (O2-.) during the electron transfer process. The enzymatic activity of mitochondrial manganese superoxide dismutase (MnSOD) converts O2-. to hydrogen peroxide (H2O2) which may then diffuse to the cytoplasmic compartments where glutathione peroxidase and catalase convert H2O2 to H2O. However, H2O2 can interact with Fe2+ or Cu+ to generate hydroxyl radical (OH.), a highly reactive free radical that can induce lipid peroxidation and oxidative damage to proteins and DNA. Mitochondrial uncoupling proteins (UCP) function as H+ leak channels which decrease mitochondrial membrane potential results in decreased generation of O2-. and ATP. Several mitochondrial proteins are involved in regulating movement of Ca2+ into and out of the mitochondria including the Ca2+ uniporter which moves Ca2+ into the mitochondrial matrix and the Ca2+ antiporter which extrudes Ca2+ into the cytosol. In addition, movement of K+ through ATP-sensitive potassium channels (KATP) in the inner membrane can result in decreased mitochondrial Ca2+ uptake. An important transmembrane protein complex which includes the voltage-dependent anion channel (VDAC) forms large permeability transition pores (PTP). The PTP open during the process of apoptosis resulting in the release of cytochrome c into the cytoplasm. Several cytoplasmic proteins may also interact with mitochondrial membranes resulting in a change its permeability including Bcl-2 and BH-only proteins such as Bax, Bid and Bik. Finally, there are interactions between mitochondria and the endoplasmic reticulum (ER) such that Ca2+ released through ER IP3 receptors and ryanodine receptors (RyR) is rapidly transferred into mitochondria. On the other hand, cytochrome c released from mitochondria can trigger the release of Ca2+ from the ER.