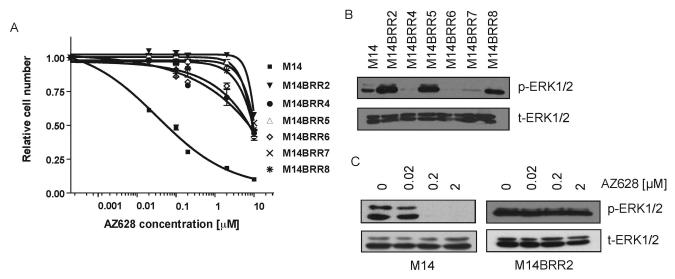
Figure 1. M14-derived AZ628-resistant (M14BRR) clones display elevated levels pERK1/2 and uncoupling of ERK signaling from BRAF.
(A) Dose-response curves of M14 and six M14BRR clones treated with the indicated concentrations of AZ628. The fraction of viable cells is expressed relative to untreated controls. Error bars represent the standard deviation from the mean.
(B) Immunoblots with the indicated antibodies demonstrating that M14BRR clones exhibit elevated basal activation of ERK1/2 compared to parental M14 cells. Cell lysates from M14 and six independently-generated M14BRR clones maintained in the presence of 2 μM AZ628 were collected.
(C) Immunoblots with the indicated antibodies demonstrating that M14BRR cells maintain ERK phosphorylation in the presence of AZ628. Cell lysates from M14 and AZ628-resistant clone (M14BRR2) were collected following 2 hour treatment with the indicated concentrations of AZ628.