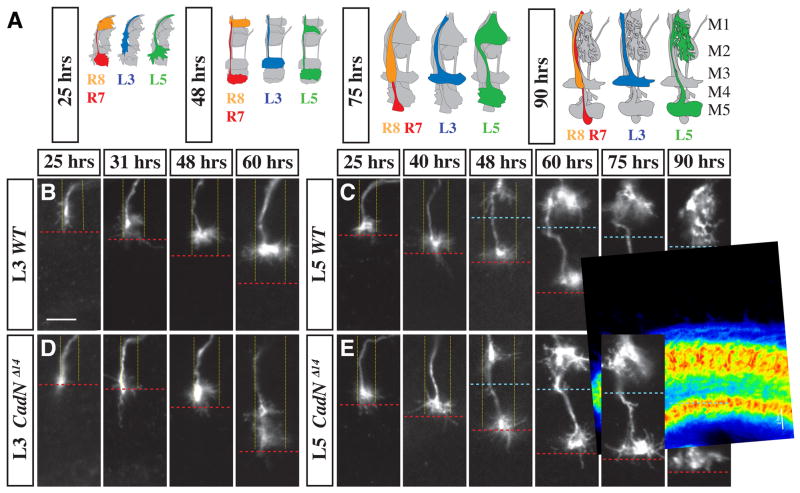
Figure 2. CadN is required for specific steps of L3 and L5 targeting.
(A) Schematic of wild-type L3, L5, R7 and R8 growth cones at different developmental stages (indicated as hrs APF). In each cartoon, all R cell and lamina neuron processes in a medulla column are shown in grey with either L3 (blue), L5 (green) or both R7 (red) and an R8 (orange) highlighted. (B–E) Medulla terminals of single wild-type (B,C) and CadNΔ14 mutant (D,E) (L3 [B,D] and L5 [C, E]) neurons at indicated times APF. Note the CadN-dependent lateral spread of L3 growth cones within their layer at early- to midpupal stages and the late pupal extension of L5 processes into M2. Column boundaries (fine yellow dotted lines) and M2/M3 layer boundary (blue dashed line) are based on anti-CadN staining and the R7 layer position (red dashed lines) on mAb24B10 staining (not shown). L3 and L5 clones were visualized by MARCM with dacFLP and the 9–9 GAL4 marker plus two copies of UAS mCD8GFP (L3) or the 6–60 GAL4 marker with UAS mCD8GFP and UAS N-sybGFP (L5). Scale bar, 5 μm.